News
-
 Space
SpaceTwo privately-owned spacecraft make contact from the moon
Firefly Aerospace landed a craft safely last week, a first for a private company. But Intuitive Machines’ mission ended when its lander wound up on its side in a crater.
-
 Climate
ClimateWarming is chasing cloud forests steadily uphill
Cloud forests are biodiversity hot spots and crucial water sources. But climate change and deforestation are shrinking their range, new data show.
By Douglas Fox -
 Animals
AnimalsHow a Labrador retriever’s genes might affect the dog’s obesity risk
Understanding the genetics of Labrador retriever obesity may help dog owners mitigate their best friend’s weight gain.
By Alex Viveros -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceJuno reveals dozens of lava lakes on Jupiter’s moon Io
NASA’s Juno spacecraft identifies over 40 enormous lava lakes on Io, shedding light on the extreme volcanism sculpting Jupiter’s moon.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTreating male partners along with women may help stop bacterial vaginosis
In a clinical trial, treating both partners in a relationship significantly reduced the likelihood of recurrence of bacterial vaginosis.
-
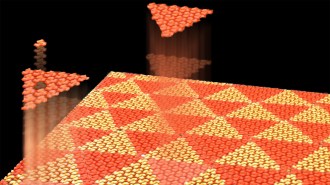 Math
MathThe einstein tile rocked mathematics. Meet its molecular cousin
Chemists identify a single molecule that naturally tiles in nonrepeating patterns, which could help build materials with novel electronic properties.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyHuman ancestors made the oldest known bone tools 1.5 million years ago
The excavation of bone tools at Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania expands the range of ancient hominids’ cultural innovations.
By Bruce Bower -
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe Milky Way’s black hole is constantly bubbling
The disc of plasma surrounding the black hole at the heart of the Milky Way is constantly emitting flares both large and small.
-
 Animals
AnimalsCrickets and flies face off in a quiet evolutionary battle
Male crickets in Hawaii softened their chirps once parasitic flies started hunting them. Now, it seems, the flies are homing in on the new tunes.
By Jake Buehler -
 Physics
PhysicsThe sound of clapping, explained by physics
The “Helmholtz resonator” concept explains the frequencies of sound produced by clapping the hands together in different configurations.
-
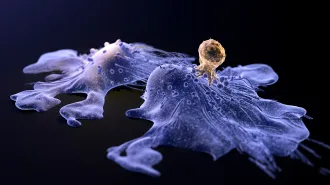 Genetics
GeneticsA child who got CAR-T cancer therapy is still disease-free 18 years later
The long-term survival of a patient with neuroblastoma suggests the personalized cancer treatment may work for solid tumors, not just blood cancers.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe universe’s first supernovas probably produced water
Water may have formed less than 200 million years after the Big Bang, suggesting some conditions for life existed far earlier than previously thought.