News
-
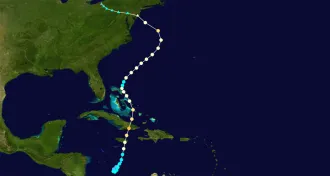 Climate
ClimateNo more Superstorm Sandys expected for a long time
Future conditions less likely to steer hurricanes directly into the East Coast, analysis suggests.
By Erin Wayman -
 Animals
AnimalsTraveling with elders helps whooping cranes fly straight
Rare data show birds get more efficient the more they migrate along route between Wisconsin and Florida.
By Susan Milius -
 Tech
TechStretchy, see-through material conducts electricity
Simple new device could find use in loudspeakers, artificial muscles or soft robots.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Psychology
PsychologyPoverty may tax thinking abilities
Scarce funds reduce mental abilities of U.S. shoppers and Indian farmers, experiments suggest.
By Bruce Bower -
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe sun’s older twin, 250 light-years away
Almost twice as ancient, the distant star gives a glimpse of the sun's future.
By Andrew Grant -
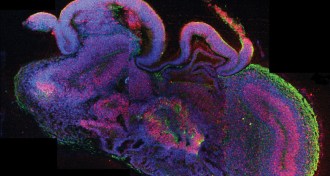 Life
LifeTiny human almost-brains made in lab
Stem cells arrange themselves into a version of the most complex human organ.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceTitan becomes even more enigmatic
Thick, rigid crust of ice encases Saturn's largest moon, perplexing scientists.
By Andrew Grant -
 Climate
ClimateGlobal warming hiatus tied to cooler temps in Pacific
Average air temperatures' rise has paused, but not stopped, because of normal variation in ocean temperatures.
By Erin Wayman -
 Life
LifeA fight between gut parasites means a win for people
Worms and Giardia can antagonize each other in the human intestinal tract, study of people in the Amazon suggests.
-
 Humans
HumansBabies learn words before birth
Brain responses suggest infants can distinguish distinct words from altered versions that they learned in the womb.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyBehavioral research may overstate results
'Soft' sciences inflate support for what scientists expected to find, data check suggests.
By Bruce Bower -
 Earth
EarthBreakups maintain barchan dune fields, somehow
Two new theories try to explain how the crescent-shaped sand mountains persist.
By Erin Wayman