News
-
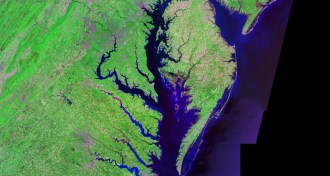 Oceans
OceansExtremely salty water is at least 100 million years old
Supersaline sediments off East Coast shed light on Atlantic Ocean’s early history.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBacteria may transfer mom’s stress to fetus
Expecting mice under psychological pressure passed different mix of microbes to their pups, affecting the babies’ brains.
-
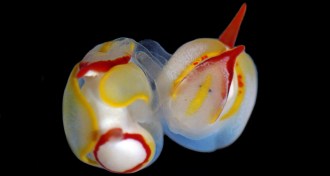 Animals
AnimalsSea slug mating features a stab in the head
Newly discovered hermaphroditic sea slug deploys specialized needle-thin organ for injections near the eyes.
By Susan Milius -
 Microbes
MicrobesSurprising metals found in microbes
Scientists discover the first case of an organism needing a rare earth element for survival.
-
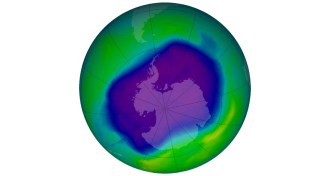 Climate
ClimateHistorical events linked to changes in Earth’s temperature
Ozone treaty, wars and Great Depression influenced global warming rate, scientists find.
-
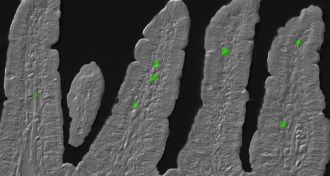 Life
LifeImmune system follows circadian clock
Mice with jet lag have boosted supply of cells linked to inflammation.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMeteor explosions like this year’s Russian fireball more common than thought
Chelyabinsk-sized rocks may come to Earth every 30 years, on average.
By Andrew Grant -
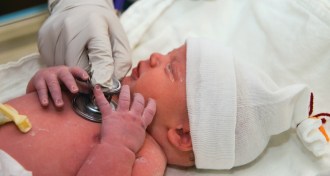 Life
LifeNewborns’ weak immunity may allow helpful bacteria to gain a foothold
Though infant immune systems raise risk of infection, they also allow good microbes into the body, study in mice shows.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAutism may be detectable in baby’s first months of life
Infants later diagnosed with an autism spectrum disorder lose tendency to gaze at others’ eyes during first half-year, researchers find.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyBillions and billions of Earth-sized planets call Milky Way home
Using Kepler data, astronomers estimate that a sizeable fraction of the galaxy’s sunlike stars have Earth-sized planets that could support liquid water.
By Andrew Grant -
 Earth
EarthGreenhouse gas injections may unleash earthquakes
Plans to pump carbon dioxide into the ground to mitigate climate change could create other problems.
By Beth Mole -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain enables sight without light
Sensory cross talk may underlie ability to see one’s own hand moving when it’s pitch black.
By Bruce Bower