News
-
 Psychology
PsychologyStereotypes might make ‘female’ hurricanes deadlier
Precautions may get shelved by those in the path of severe storms with feminine names, leading some to suggest that storms should be named after animals.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBrain’s support cells play role in hunger
Once considered just helpers for neurons, astrocytes sense the hormone leptin and can change mice’s appetites.
-
 Life
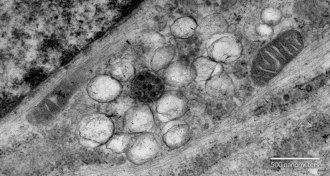
LifeDrug candidate takes new aim at MERS
An experimental drug that shuts down construction of virus-making factories could become a new weapon against MERS.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Tech
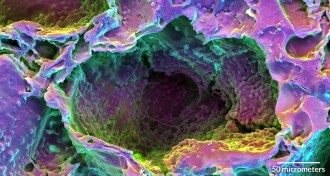
TechLasers heal damaged rodent teeth
Handheld laser spurs stem cells into action, regrowing dentin in drilled teeth.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyFirst pants worn by horse riders 3,000 years ago
A new study indicates horse-riding Asians wove and wore wool trousers by around 3,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsReef fish get riled when intruders glow red
A male fairy wrasse gets feisty when he can see a rival’s colorful fluorescent patches.
By Susan Milius -
 Climate
ClimateViolent storms may shatter sea ice
Tall waves’ effect on sea ice hints at troubled water in the future.
By Beth Mole -
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsProton’s magnetic properties pinned down
A precise measurement of a proton’s magnetic properties could help reveal subtle differences between matter and antimatter.
By Andrew Grant -
 Life
LifeStarchy foods more filling than fiber, lab tests suggest
Tests of gut microbe digestion of potato starch and fiber suggest that moving away from grass-heavy ancestral diets may not be the reason for obesity epidemic.
-
 Life
LifeDrab female birds had more colorful evolution
Males weren’t the main players in evolution of sex differences in avian plumage.
By Susan Milius -
 Astronomy
AstronomySun shines new life on Kepler space telescope
NASA approved a proposal to bring the crippled Kepler spacecraft back to life, using sunlight as balance to help the telescope search for planets and more.
-
 Psychology
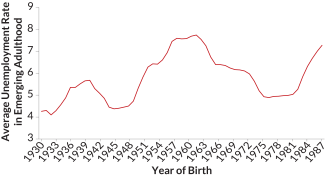
PsychologyRecessions take a lasting toll on narcissism
Coming of age in hard economic times makes people less likely to feel superior and entitled later in life.
By Bruce Bower