News
-
 Health & Medicine
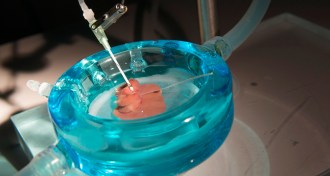
Health & MedicineSupercooling makes livers for transplants last longer
Supercooling a rat liver for transplant greatly increased an organ’s survival time outside the body, potentially opening the door for global allocation of human organs.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAutism may carry a benefit: a buffer against Alzheimer’s
Brain plasticity of people with autism may protect them from Alzheimer’s disease, scientists propose.
-
 Life
LifeTibetans live high life thanks to extinct human relatives
DNA shared by modern-day Tibetans and extinct Denisovans suggests people picked up helpful genes through interbreeding with other hominids.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyTablet devices help kids with autism speak up
Talking iPads may help break the near-silence of some kids with autism.
By Bruce Bower -
 Environment
EnvironmentPlastic goes missing at sea
A survey of the world’s oceans finds far less polymer trash than expected, and researchers don’t know where the rest of the plastic is.
By Sam Lemonick -
 Life
LifeNear reefs, microbial mix dictated by coral and algae
A reef’s dominant organism, coral or algae, may determine what kind of bacteria live there.
-
 Neuroscience
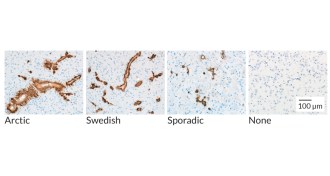
NeuroscienceAlzheimer’s disease may come in distinct forms
Mouse experiments, if confirmed in people, imply that Alzheimer’s disease treatment should be personalized.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyMagnetic bubbles could shield astronauts from radiation
With help from plasma and a magnet, solar storms' dangers would lessen on long space trips.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsMysterious neurotoxin may help flatworms kill prey
Tetrodotoxin, the deadly chemical in pufferfish, could help flatworms transform their earthworm prey into puddles of goo.
By Beth Mole -
 Neuroscience
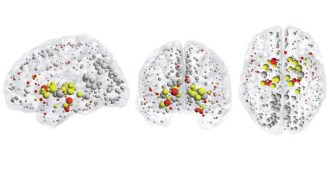
NeuroscienceBusy brain hubs go awry in disorders, study suggests
Schizophrenia, Alzheimer’s and other brain disorders may occur when the brain’s most active hubs are damaged.
-
 Life
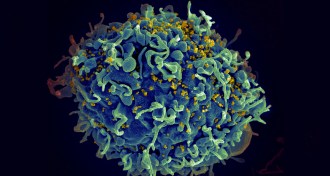
LifeHIV hides in growth-promoting genes
The discovery that HIV can trigger infected cells to divide means scientists may need to rethink strategies for treating the virus that causes AIDS.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHidden heart rhythm problem may underlie some strokes
In two clinical studies, people who had had strokes with no trigger sometimes also had undiagnosed atrial fibrillation.
By Nathan Seppa