News
-
 Space
SpaceThe nearest single star to Earth has four small planets
Last year, astronomers announced that a planet orbits Barnard’s star. Now, researchers have confirmed the existence of three more.
-
 Space
SpaceTwo astronauts stuck in space for 9 months have returned to Earth
Astronauts Suni Williams and Butch Wilmore’s extended stay in the International Space Station will add to what we know about how space affects health.
-
 Cosmology
CosmologyNew baby pictures of the universe deepen a cosmic mystery
Cosmic microwave background data support cosmology’s standard model but retain a mystery about the universe’s expansion rate.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSome of Sydney’s koalas are chlamydia-free, but still at risk
Southwestern Sydney's koalas have avoided the chlamydia outbreak threatening the entire species. But their isolation has left them extremely inbred.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsThe mystery of how iguanas crossed the Pacific Ocean may be solved
The iguanas' 8,000-kilometer trip — one-fifth of the Earth’s circumference — is the longest made by a flightless land vertebrate.
By Jake Buehler -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMeasles is spreading. Here’s what experts say you should know
The uptick in measles cases has left many people wondering about early signs of measles, whether they need an updated vaccine and treatment options.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTherapy dogs can ease young patients’ anxiety in the emergency room
A clinical trial found that spending about 10 minutes with a therapy dog reduced patients’ anxiety in a pediatric emergency room.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNarwhals may use their iconic tusks to play
Videos show narwhals using their tusks in several ways, including prodding and flipping a fish. It’s the first reported evidence of the whales playing.
-
 Space
SpaceThe Blue Ghost lander just witnessed a lunar eclipse — from the moon
The privately-owned lander turned its cameras toward Earth as our planet cast its shadow over the moon. It’s not the first spacecraft to do so.
-
 Life
LifeDark coats may have helped the earliest mammals hide from hungry dinosaurs
During the age of dinosaurs, early mammals probably lacked the stripes and spots of their modern relatives, having uniformly dark, drab coats.
By Jake Buehler -
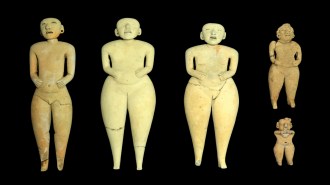 Archaeology
ArchaeologyThese ancient Maya-era puppets may have been used in rituals
The puppets, unearthed in El Salvador, have movable heads, strange facial expressions and may have been dressed for ritual roles.
By Tom Metcalfe -
 Chemistry
ChemistryA new iron compound hints ‘primordial’ helium hides in Earth’s core
Earth’s core could contain helium from the early solar system. The noble gas tucks into gaps in iron crystals under high pressure and temperature.
By Skyler Ware