News
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHints about schizophrenia emerge from genetic study
From thousands of genomes, researchers pinpoint dozens of DNA changes that may underlie schizophrenia
-
 Animals
AnimalsTermite soldiers locate battles with vibrational clues
To locate invasions, termite soldiers listen for millisecond-long delays in vibrational distress signals sent out by other soldiers.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
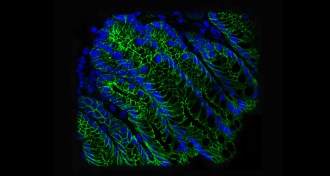
Health & MedicineCarbs and gut microbes fuel colon cancer
Western nations experience high levels of colon cancer, and carbo-loading gut microbes might explain why, says a new study in mice.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Earth
EarthSandstone structures form without cement
Lasting sandstone structures form when weighed-down sand locks into stable formations, researchers find in laboratory experiment.
-
 Tech
TechWax-coated plastic morphs between soft and stiff
Heat-controlled materials could serve as skeleton for shape-shifting robots.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOrganic foods may contain extra antioxidants
Contrary to previous studies, a new analysis finds that organic crops have nutritional benefits over conventionally grown foods.
By Beth Mole -
 Life
LifePregnancy disorder shares aspects with Alzheimer’s
Misfolded proteins, the hallmark of Alzheimer’s and mad cow diseases, are found in urine of women with preeclampsia.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceObese women struggle to learn food associations
In a lab experiment, women fail to connect color signal with tasty reward, a deficit that may contribute to obesity.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyVoyager may not have entered interstellar space, after all
Two scientists argue that Voyager 1 space probe is still in solar bubble, despite NASA’s announcements to the contrary.
By Andrew Grant -
 Plants
PlantsWine corks may owe quality to gene activity
Discovery of genes that distinguish superior stoppers from inferior ones could help reverse recent global downturn in quality.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Neuroscience
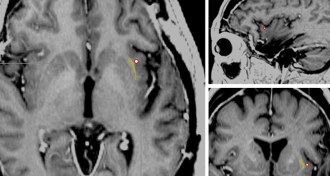
NeuroscienceElectrode turns consciousness on and off
Woman lost awareness, though appeared awake, when her brain was stimulated near an area called the claustrum.
-
 Life
LifeDomesticated animals’ juvenile appearance tied to embryonic cells
Mild defects in embryonic cells could explain physical similarities along with tameness across domesticated species.