News
- Animals
This tool-using cow defies expectations for bovine braininess
Veronika the cow uses a brush as a tool to scratch herself, revealing rare problem-solving skills and expanding what we know of tool use in animals.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThis fish may play a hole in its head like a drum
The rockhead poacher is a little fish with a big pit in its head. The divot may be like a drum, making sound that rises above a chaotic, nearshore din.
By Jake Buehler -
 Earth
EarthA long-lost tectonic fragment may be shaking Northern California
Seismic tremors reveal a shallow fragment of an ancient tectonic plate beneath Northern California, helping explain damaging earthquakes near the surface.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineColor blindness hides a key warning sign of bladder cancer
A large U.S. health records study suggests that difficulty seeing blood in urine may put color-blind patients at higher risk.
By Elie Dolgin -
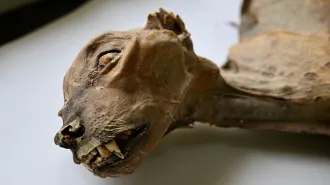 Animals
AnimalsHow cheetah mummies could help bring the species back to Arabia
Arabian cheetah mummies' DNA reveals that the long-lost population could be closely replaced by a cheetah population in northwestern Africa.
By Jake Buehler -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyThis dino’s fossil claw suggests it snatched eggs, not insects
A 67-million-year-old claw fossil reveals a new dinosaur species that may have used its hand spikes to snatch and pierce eggs.
-
 Plants
PlantsPlants packed close enough to touch are more resilient to stress
Signals transmitted via leaves can warn neighboring plants of stressful events, making the group collectively more resilient than plants in isolation.
-
 Climate
ClimateEarth’s last 3 years were its hottest on record
An analysis of global climate data shows sustained warming even as El Niño faded.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyThis ancient pottery holds the earliest evidence of humans doing math
Flower designs on 8,000-year-old Mesopotamian pots reveal a “mathematical knowledge” perhaps developed to share land and crops, archaeologists say.
By Tom Metcalfe -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBotox could be used to fight snakebite
A study on rabbits dosed with viper venom suggests that botulinum toxin may alleviate some effects of snakebite, possibly by dampening inflammation.
By Jake Buehler -
 Physics
PhysicsQueen bumblebees are poor foragers thanks to sparse tongue hair
The density of fine hairs on bumblebees’ tongues determines how much nectar they can collect — and workers put queen bees to shame.
-
 Plants
PlantsIn a new kind of plant trickery, this yam fools birds with fake berries
Black-bulb yam’s mimicry tricks birds into spreading its berrylike clones. The plant's novel strategy helps it spread without seeds or sexual reproduction.