News
-
 Life
LifeElectric eels remote-control nervous systems of prey
Electric eels’ high-voltage zaps turn a prey fish against itself, making it freeze in place or betray a hiding place.
By Susan Milius -
 Planetary Science
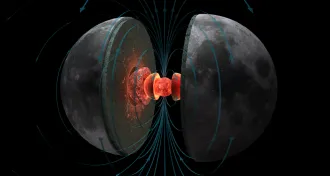
Planetary ScienceAncient moon’s mega magnetic field explained
Apollo-era moon rocks reveal ancient lunar magnetic field was at least as powerful as the one surrounding modern Earth.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceCarbon supplants silicon in electronic medical sensors
Prototypes of electronic medical devices constructed from organic materials are noninvasive yet offer similar performance as silicon-based health sensors.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyHuman ancestors engraved abstract patterns
Indonesian Homo erectus carved zigzags on a shell at least 430,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Cosmology
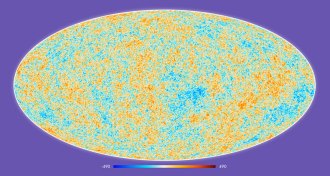
CosmologyMost precise snapshot of the universe unveiled
New results from the Planck satellite provide the most detailed look yet of the makeup of the universe.
-
 Life
LifeTadpole eye transplant shows new way to grow nerves
Wiring replacement organs into the body may be as easy as discharging a biological battery, new experiments with tadpoles suggest.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceComet lander’s exploration cut short
The comet lander Philae made history with its touchdown on comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko, but a series of small hiccups prevented the robot from recharging its batteries, giving it only about 57 hours to explore the alien world.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTurning the immune system on cancer
A new class of drugs uncloaks tumors in some patients, awakening home-grown cells to fight several cancer types.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyGolden Fleece myth was based on real events, geologists contend
Jason’s legend grew out of long-distance trade with people who used sheepskins to collect gold.
By Bruce Bower -
 Oceans
OceansRobotic subs reveal thicker Antarctic sea ice
New measurements by robotic subs suggest that scientists have underestimated Antarctic sea ice thickness.
-
 Physics
PhysicsNegative mass might not defy Einstein
Repulsive matter could have played a role in the early universe, a computational study finds.
By Andrew Grant -
 Chemistry
ChemistryRadioactive fuel turns to goo during nuclear meltdown
Experiments reveal the atomic rearrangements that occur within uranium dioxide when nuclear reactors fail.
By Beth Mole