News
-
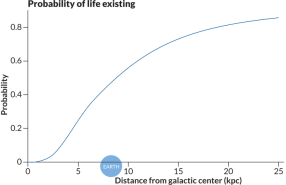 Astronomy
AstronomyGamma-ray bursts may repeatedly wipe out life
Brief bursts of high-energy radiation may sterilize most planets across the universe, hampering the chances for widespread intelligent life.
By Andrew Grant -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceSolar wind probably leaches Mars’ lower atmosphere
Initial results from NASA's MAVEN probe may help explain how Mars has lost its atmosphere: The solar wind penetrates the Red Planet’s atmosphere and fuels escaping gas.
-
 Math
MathMath to match pedestrian behavior is all about timing
The best-ever simulation of pedestrians moving through a crowd relies on a new formula that encapsulates people’s ability to anticipate collisions.
By Andrew Grant -
 Life
LifeNew tree of life confirms strange history of birds
A genetic analysis supports some odd groupings in the bird tree of life, showing a lot of convergent evolution in avian history.
By Susan Milius -
 Earth
EarthMega volcanism indicted in dinosaur demise
Precision dating strengthens idea that climate-altering Deccan volcanism contributed to dinosaur extinction.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGene variant linked to robust flu vaccine response
Targeting an immune signaling protein called interleukin-28B might boost protection generated by flu shots.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHallucinated voices’ attitudes vary with culture
Culture puts good or bad spin on voices heard by people with schizophrenia.
By Bruce Bower -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceRosetta casts doubt on comets as Earth’s water providers
Water in comet 67P’s thin, hazy atmosphere doesn’t chemically match Earth’s oceans, suggesting that asteroids, not comets, brought water to the planet.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsNew type of stem cells, fuzzy and flexible
A new way to make stem cells produces fuzzy cells that appear as flexible as other types of stem cells, but are easier to grow in the lab and avoid ethical issues.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMolecule impairs brain cells that fail in Alzheimer’s
In mice, blocking a molecule on immune cells allowed them to mop up the type of protein buildup seen in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCells in groups may promote cancer’s spread
Cellular gangs, not individuals, form distant tumors from breast malignancies, a new study finds.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryEarly asteroid impacts may have aided life’s origin
RNA ingredients found in laser-induced simulation of explosions.
By Beth Mole