News
-
 Physics
PhysicsRogue waves don’t always appear unannounced
Scientists may be able to forecast the arrival of anomalously large ocean swells, suggest scientists who analyzed the moments before rogue water waves and freak light flashes.
By Andrew Grant -
 Climate
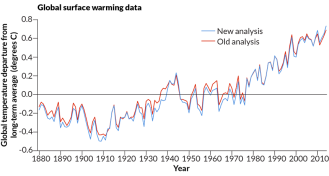
ClimateGlobal warming ‘hiatus’ just an artifact, study finds
Skewed data may have caused the appearance of the recent global warming hiatus, new research suggests.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFemale’s nose blocks scent of a male
When a female mouse is in an infertile stage of her reproductive cycle, her nose cells don’t alert her brain to the presence of a potential mate.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyTriceratops relative reveals dino diversity
A newly discovered relative of Triceratops provides new insight into the evolution of horned dinosaurs.
-
 Genetics
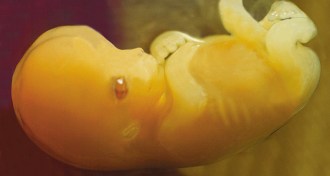
GeneticsDNA tags mostly deleted in human germ cells
Human embryos come with some heavy-duty erasers. Chemical tags on DNA get mostly wiped out in the womb.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsPregnant male pipefish not so great at giving embryos oxygen
During male pregnancy, pipefish embryos can get stunted by low oxygen in dad’s brood pouch.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
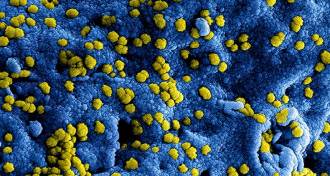
Health & MedicineDeadly MERS spreads in small cluster in South Korea
Thirty people have MERS virus in the South Korean outbreak, including China’s first case.
-
 Planetary Science
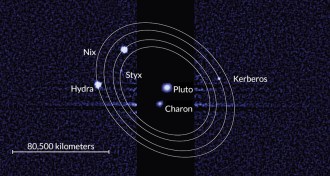
Planetary SciencePluto’s four littlest moons probably born in a crash
On the eve of the arrival of the New Horizons spacecraft, Pluto’s tiny moons hint at a common origin.
-
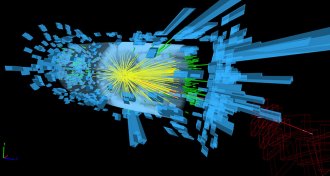 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsLHC set to see beyond Higgs
Physicists hope a revamped Large Hadron Collider will discover new particles and forces that could help explain dark matter and other mysteries of the universe.
By Andrew Grant -
 Environment
EnvironmentMystery toxins in tainted New Zealand honey nabbed
Sweet and stealthy toxins have been caught sticky-handed, potentially solving a decades-long mystery of tainted honey in New Zealand.
By Beth Mole -
 Climate
ClimateTitanic typhoons are in the forecast
Warming subsurface water in the Pacific will boost average typhoon intensity 14 percent by 2100, new research predicts.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyIn another universe, free-range planets could host life
If other universes exist, then those with denser galaxies might harbor a larger fraction of habitable worlds.