News
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyTooth, jaw fossils tell tale of North America’s last nonhuman primates
Oregon fossils provide new clues to North America’s last nonhuman primates.
By Bruce Bower -
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePotential pain treatment’s mechanism deciphered
Scientists have new insight as to how a class of environment-sensing bone marrow cells can help safely relieve pain.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsMutation-disease link masked in zebrafish
Zebrafish study shows organisms can work around DNA mutations.
-
 Physics
PhysicsSwimming bacteria remove resistance to flow
The collective motion of swimming bacteria can virtually eliminate a water-based solution’s resistance to flow.
By Andrew Grant -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyAncient comb jellies might have had skeletons
Soft and filmy today, comb jellies might once have had rigid skeletons.
By Susan Milius -
 Anthropology
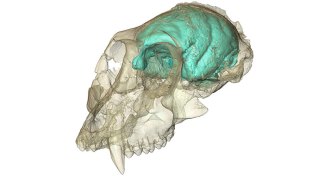
AnthropologyMonkey’s small brain shows surprising folds
An ancient monkey’s tiny brain developed folds, raising questions about primate evolution.
By Bruce Bower -
 Climate
ClimateBumblebee territory shrinking under climate change
Climate change is shrinking bumblebee habitat as southern territories heat up and bumblebees hold their lines in the north.
By Beth Mole -
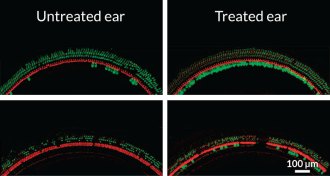 Genetics
GeneticsGene therapy restores hearing in mice
Scientists have used gene therapy to restore hearing in deaf mice.
-
 Climate
ClimateGreenland’s out-of-sync climate explained
Small variations in the sun’s activity cause big changes in Greenland’s temperatures decades later by altering ocean currents, new research suggests.
-
 Life
LifeAge isn’t just a number
Getting old happens faster for some, and the reason may be in the blood.
-
 Physics
PhysicsMagnetic test boosts case for record-setting superconductor
New measurements bolster the case that hydrogen sulfide is superconducting at about 200 kelvins, roughly 40 kelvins higher than any other known material.
By Andrew Grant