News
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary SciencePhobos starting to crack under pressure
Grooves that wrap around Phobos show that the Martian moon is starting to crack from stress.
-

-
 Planetary Science
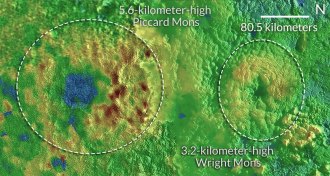
Planetary SciencePluto continues to deliver surprises
Ice volcanoes, young landscapes and twirling moons are just a few more surprises from Pluto.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSimple steps can offer health benefits
Studies find that even small changes in eating habits and movement can lower risk of heart disease.
By Laura Beil -
 Health & Medicine
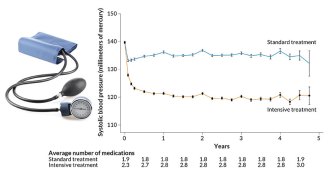
Health & MedicineDropping blood pressure to 120 lowers heart woes, data confirm
Aggressive treatment to lower systolic blood pressure to 120 reduces risk of heart attack, but causes some side effects.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAntibodies to fight Alzheimer’s may have unexpected consequences
Alzheimer’s-targeted antibodies make neurons misbehave even more, a study of mice shows.
-
 Life
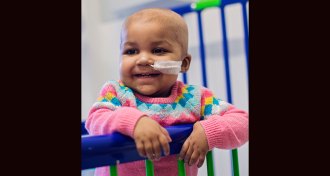
LifeGene editing helps a baby battle cancer
Doctors used molecular scalpels to tweak T cells to target leukemia but not harm the patient.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient hominids used wooden spears to fend off big cats
Saber-toothed cat remains suggest ancient hominids used wooden spears as defensive weapons.
By Bruce Bower -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyLand life spared in Permian extinction, geologists argue
New rock layer dating in South Africa’s Karoo Basin suggests that extinctions of land species didn’t coincide with the Permian extinction around 252 million years ago.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryTricky element isolated from spent nuclear fuel
A new chemical technique makes it easier to extract the radioactive element americium from used nuclear fuel, potentially paving the way for better ways to reprocess and recycle nuclear waste.
By Andrew Grant -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMAVEN mission finding clues to Mars’ climate change
Intense solar storms in the past might have stripped Mars of its water as well as much of the rest of its atmosphere.
-
 Climate
ClimateKangaroo farts may not be so eco-friendly after all
Kangaroos fart methane, but not much thanks to the metabolism of gut microbes