News
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyMiddleweight black hole suspected near Milky Way’s center
A gas cloud in the center of the galaxy might be temporarily hosting the second most massive black hole known in the Milky Way.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureJust adding pollinators could boost small-farm yields
Adding pollinators could start closing gap in yields for small farms.
By Susan Milius -
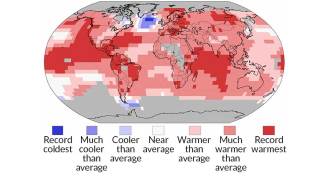 Climate
Climate2015 smashed heat records
Spurred by global warming and a “super El Niño,” 2015 now ranks as the warmest year since record-keeping began in 1880.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceTime running out on comet lander
Philae’s days are numbered as temperatures on comet 67P drop and attempts to communicate with the lander fail.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAttack 10,000 years ago is earliest known act of warfare
Human skeletons unearthed in East Africa show signs of a roughly 10,000-year-old lethal raid.
By Bruce Bower -
 Humans
HumansNo fairy tale: Origins of some famous stories go back thousands of years
Pairing folktales with ancient languages shows that at least a few folktales originated thousands of years ago.
-
 Climate
ClimateAtmospheric tides alter rainfall rate
Atmospheric tides caused by the moon’s gravitational pull ever-so-slightly alter rainfall rates on Earth by producing rises and falls in atmospheric pressure.
-
 Life
LifeSearch is on for missing pieces in puzzle of male genital diversity
The debate over extreme diversity of male genitalia needs to rethink the female side. And the landscape.
By Susan Milius -
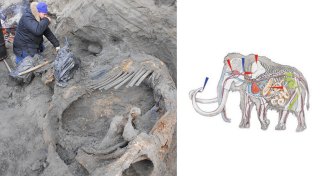 Archaeology
ArchaeologyHumans visited Arctic earlier than thought
Human weapon injuries on mammoth bones show humans were in the Arctic up to 15,000 years earlier than researchers thought.
-
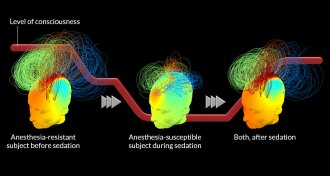 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMeasuring brain waves may help predict a patient’s response to anesthesia
Brain signatures hint at whether a person will resist or succumb to anesthesia.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentPCB levels still high in Europe’s killer whales, smaller dolphins
PCBs banned for decades still show up at extremely high concentrations in Europe’s killer whales and other dolphins.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeSigns of food allergies may be present at birth
Overactive immune cells may prime babies for food allergies.