News
-
 Physics
PhysicsPhysicists find atomic nucleus with a ‘bubble’ in the middle
Silicon-34 has an unusually small number of protons in its center.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryWater softeners get friendlier to health, environment
New technology softens water without adding sodium, which ends up in drinking water and contaminates the environment.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA data offer evidence of unknown extinct human relative
Melanesians may carry genetic evidence of a previously unknown extinct human relative.
-
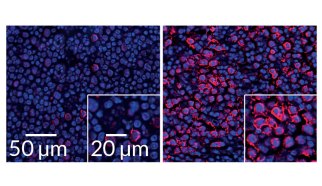 Life
LifeVirus triggers immune proteins to aid enemy
Virus-fighting proteins in the immune system can sometimes help out their targets instead.
-

-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyAncient armored fish revises early history of jaws
The fossil of a 423-million-year-old armored fish from China suggests that the jaws of all modern land vertebrates and bony fish originated in a bizarre group of animals called placoderms.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceExperts don’t agree on age of Saturn’s rings
Saturn’s rings could be almost as old as the solar system, and the Cassini craft is poised to help find out.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMice smell, share each other’s pain
Pain can jump from one mouse to another, presumably through chemicals detected by the nose.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyWild monkeys throw curve at stone-tool making’s origins
Monkeys that make sharp-edged stones raise questions about evolution of stone tool production.
By Bruce Bower -
 Genetics
Genetics‘Three-parent babies’ explained
Several in vitro techniques can produce babies with three biological parents.
-
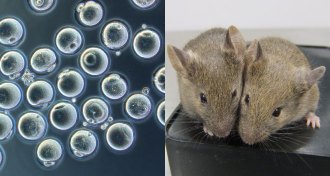 Life
LifeIn a first, mouse eggs grown from skin cells
Stem cells grown in ovary-mimicking conditions in a lab dish can make healthy mouse offspring, but technique still needs work.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceOut-of-sync body clock causes more woes than sleepiness
The ailment, called circadian-time sickness, can be described with Bayesian math, scientists propose.