News
-
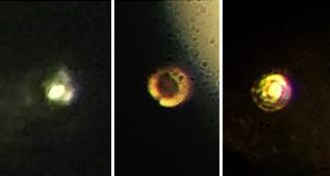 Physics
PhysicsNew claim staked for metallic hydrogen
Scientists report transforming hydrogen into a metal at high pressure, but some experts dispute the claim.
-
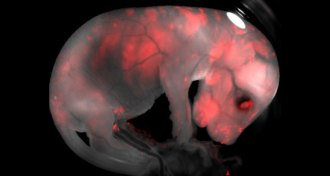 Life
LifeMouse cells grown in rats cure diabetes in mice
Mixing cells of two species produces pig and cattle embryos with some human cells.
-
 Physics
PhysicsChemists strike gold, solve mystery about precious metal’s properties
A longstanding puzzle about gold’s properties has been solved with more complex theoretical calculations.
-
 Life
LifeWhat a mosquito’s immune system can tell us about fighting malaria
Immune system messengers carried in microscopic sacs help mosquitoes fend off malaria, new research suggests.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsIn debate over origin of fairy circles, both sides might be right
Odd bare spots called fairy circles in African grasslands might be caused by both termites and plants.
By Susan Milius -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyCancer studies get mixed grades on redo tests
Replications of cancer studies fail to reproduce some results.
-
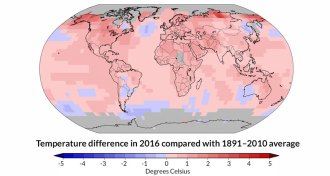 Climate
ClimateFor three years in a row, Earth breaks heat record
Spurred by climate change and heat from a strong El Niño, 2016 was the hottest year on record.
-
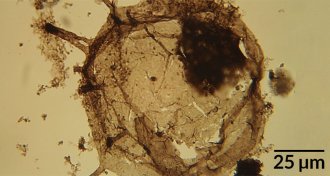 Earth
EarthCoastal waters were an oxygen oasis 2.3 billion years ago
Coastal waters contained enough oxygen to support complex life-forms including some animals hundreds of millions of years before fossils of such life first appear.
-
 Climate
ClimatePetrified tree rings tell ancient tale of sun’s behavior
The 11-year cycle of solar activity may have been around for at least 290 million years, ancient tree rings suggest.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePromise and perils of marijuana deserve more scientific scrutiny
Report outlines medical potential and health dangers of cannabis and its components.
By Bruce Bower -
 Chemistry
ChemistryNew molecular knot is most complex yet
The knot is woven from 192 atoms of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen and forms a triple braid with eight crossing points.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHow mice use their brain to hunt
Messages from the brain’s amygdala help mice chase and kill prey.