News
-
 Psychology
PsychologyPhysically abused kids learn to fail at social rules for success
What physically abused kids learn about rewards at home can lead to misbehavior elsewhere.
By Bruce Bower -
 Astronomy
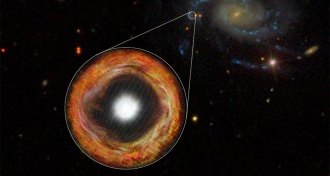
AstronomySupernova spotted shortly after explosion
Early observations of exploding star could indicate that stars become unstable as they near death.
-
 Oceans
OceansFleeting dead zones can muck with seafloor life for decades
Low-oxygen conditions can fundamentally disrupt seafloor ecosystems and increase carbon burial, new research shows.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRicin poisoning may one day be treatable with new antidote
Mice treated with a blend of antibodies survived even when treated days after exposure to ricin.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
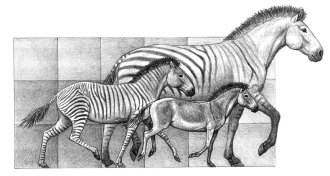
LifeHorses buck evolutionary ideas
Horse evolution doesn’t fit classic scenario of trait evolution.
-
 Life
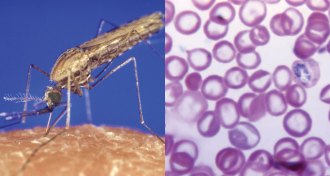
LifeMalaria molecule makes blood extra-alluring to mosquitoes
Scientists have identified a molecule that draws mosquitoes to malaria-infected blood.
-
 Animals
AnimalsYoung penguins follow false food cues
Juvenile African penguins are being trapped in barren habitats, led astray by biological cues that are no longer reliable because of human activity.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsNumber of species depends how you count them
Genetic evidence alone may overestimate numbers of species, researchers warn.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyMiddling black hole may be hiding in star cluster
A black hole with about 2,200 times the mass of the sun has been detected. If confirmed, it could represent a new type of gas-starved black holes and hint at how supermassive ones may form.
-
 Climate
ClimateHot nests, not vanishing males, are bigger sea turtle threat
Climate change overheating sea turtle nestlings may be a greater danger than temperature-induced shifts in their sex ratios.
By Susan Milius -
 Psychology
PsychologyLong-lasting mental health isn’t normal
Those who stay mentally healthy from childhood to middle age are exceptions to the rule.
By Bruce Bower -
 Earth
EarthOxygen flooded Earth’s atmosphere earlier than thought
The Great Oxidation Event that enabled the eventual evolution of complex life began 100 million years earlier than once thought, new dating of South African rock suggests.