News
-
 Health & Medicine
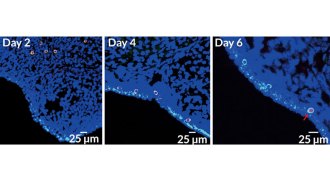
Health & MedicineTransplanted stem cells become eggs in sterile mice
Sterile mice that received transplanted egg-making stem cells were able to have healthy babies.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentWhen it’s hot, plants become a surprisingly large source of air pollution
During a heat wave, trees and shrubs can sharply raise ozone levels, a new study shows.
-
 Animals
AnimalsOrangutans take motherhood to extremes, nursing young for more than eight years
Weaning in orangutans has been tricky to see in the wild, so researchers turned to dental tests to reveal long nursing period.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhere you live can affect your blood pressure, study suggests
For black adults, moving out of a racially segregated neighborhood is linked to a drop in blood pressure, a new study finds.
-
 Physics
PhysicsNaked singularity might evade cosmic censor
Physicists demonstrate the possibility of a “naked” singularity in curved space.
-
 Genetics
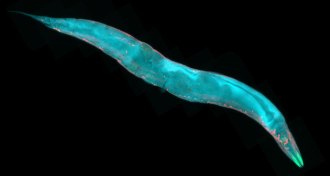
GeneticsSelfish genes hide for decades in plain sight of worm geneticists
Crossing wild Hawaiian C. elegans with the familiar lab strain reveals genes that benefit themselves by making mother worms poison offspring who haven’t inherited the right stuff.
By Susan Milius -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceWatery exoplanet’s skies suggest unexpected origin story
Compared with Neptune, HAT-P-26b’s atmosphere has few heavy elements, suggesting it formed differently than the ice giants in Earth’s solar system.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyAncient whale tells tale of when baleen whales had teeth
A 36 million-year-old whale fossil bridges the gap between ancient toothy predators and modern filter-feeding baleen whales.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘Exercise pill’ turns couch potato mice into marathoners
An experimental "exercise in a pill" increases running endurance in mice before they step foot on a treadmill.
By Laura Beil -
 Health & Medicine
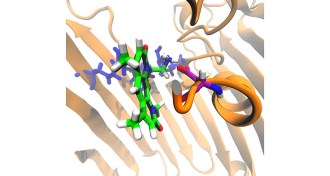
Health & MedicineNew rules for cellular entry may aid antibiotic development
A new study lays out several rules to successfully enter gram-negative bacteria, which could lead to the development of sorely needed antibiotics.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSeabirds use preening to decide how to divvy up parenting duties
Seabirds in poor condition may communicate this information to their partner by delaying or withholding preening.
-
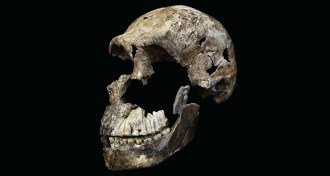 Anthropology
AnthropologyHomo naledi may have lived at around same time as early humans
South African species Homo naledi is much younger than previously thought.
By Bruce Bower