News
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyFewer big rogue planets roam the galaxy, recount shows
Jupiter-mass planets without parent solar systems are less common than astronomers thought, a new study suggests.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryRadioactive substances leave electron ‘fingerprints’ behind
A new method of nuclear forensics could make it harder to handle radioactive material in secret.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsResistance to CRISPR gene drives may arise easily
New tools for pest and disease control could become useless without improvements.
-
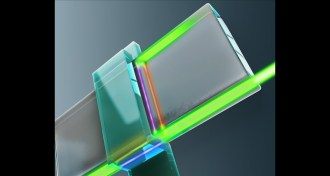 Physics
PhysicsMajorana fermion detected in a quantum layer cake
Scientists found evidence of a particle that is its own antiparticle.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCows produce powerful HIV antibodies
For the first time in any animal, researchers elicit broadly neutralizing antibodies against HIV. Cows’ antibodies could help with drug development.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThese genes may be why dogs are so friendly
Dog domestication may be the result of just a few genetic changes, including ones that made canines more interested in interacting with people.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyHumans first settled in Australia as early as 65,000 years ago
Australia may have said “G’day” to humankind thousands of years earlier than previously believed.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCommon drugs help reverse signs of fetal alcohol syndrome in rats
A thyroid hormone and a blood sugar drug affect levels of a hormone needed for brain development, study in rats shows.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDog domestication happened just once, ancient DNA study suggests
DNA of ancient canines counters idea that dogs were domesticated twice, in Europe and Asia.
-
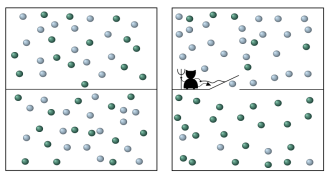 Physics
PhysicsScientists peek inside the mind of Maxwell’s demon
Scientists probe information retained by Maxwell’s demon.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceGiant mud balls roamed the early solar system
The first asteroids may have been great balls of mud, which would solve some puzzling features of meteorites.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWater bears will survive the end of the world as we know it
Water bears have a till-death-do-us-part pact with the sun, study suggests.