News
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMoon had a magnetic field for at least a billion years longer than thought
The moon’s magnetic field could have lasted until about a billion years ago.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMore U.S. adults are drinking, and more heavily
Heavy drinking and alcohol use disorders have risen in the United States, at a cost to society’s health.
-
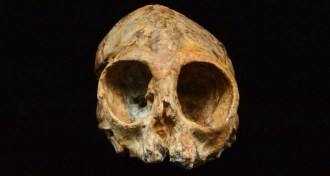 Anthropology
AnthropologyInfant ape’s tiny skull could have a big impact on ape evolution
Fossil comes from a lineage that had ties to the ancestor of modern apes and humans, researchers argue.
By Bruce Bower -
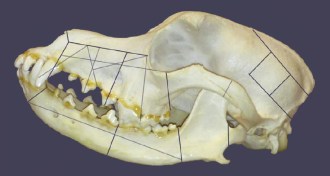 Anthropology
AnthropologySacrificed dog remains feed tales of Bronze Age ‘wolf-men’ warriors
Canine remnants of a possible Bronze Age ceremony inspire debate.
By Bruce Bower -
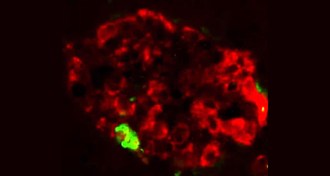 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSpread of misfolded proteins could trigger type 2 diabetes
Experiments in mice raise the question of whether type 2 diabetes might be transmissible.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsNeutrinos seen scattering off an atom’s nucleus for the first time
New type of interaction confirms that neutrinos play by the rules.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe solar system’s earliest asteroids may have all been massive
A team of astronomers says the original asteroids all came in one size: extra large.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyGiant armored dinosaur may have cloaked itself in camouflage
An armored dinosaur the size of a Honda Civic also wore countershading camouflage, a chemical analysis of its skin suggests.
-
 Life
LifeLight pollution can foil plant-insect hookups, and not just at night
Upsetting nocturnal pollinators has daylight after-effects for Swiss meadow flowers.
By Susan Milius -
 Climate
ClimateSouth Asia could face deadly heat and humidity by the end of this century
If climate change is left unchecked, simulations show extreme heat waves in densely populated agricultural regions of India and Pakistan.
-
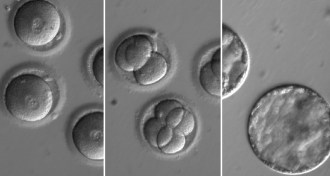 Genetics
GeneticsGene editing of human embryos gets rid of a mutation that causes heart failure
Gene editing of human embryos can efficiently repair a gene defect without making new mistakes.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceEvidence mounts for an ocean on early Venus
Not long after its birth, Venus may have rocked a water ocean, new simulations suggest.