News
-
 Environment
EnvironmentThe way poison frogs keep from poisoning themselves is complicated
Gaining resistance to one of their own toxins forced some poison dart frogs to make other genetic tweaks, too.
-
 Neuroscience
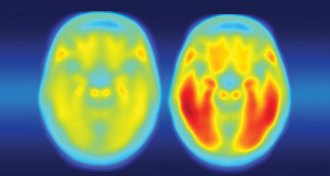
NeuroscienceGene variant linked to Alzheimer’s disease is a triple threat
A genetic risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease works on multiple aspects of the disease, researchers report.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyUltrahigh energy cosmic rays come from outside the Milky Way
The biggest cosmic ray haul ever points toward other galaxies as the source of the rays, not our own.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyShhhh! Some plant-eating dinos snacked on crunchy critters
Scientists studying dinosaur poop found that some duck-billed dinos cheated on their vegetarian diets by snacking on crustaceans.
-
 Earth
EarthIntense storms provide the first test of powerful new hurricane forecast tools
From Harvey to Maria, this year’s powerful hurricanes are giving scientists’ latest forecasting tools a trial by fire.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThis newfound hermit crab finds shelter in corals, not shells
A newly discovered hermit crab takes its cue from peanut worms and uses walking corals as a permanent shelter.
-
 Health & Medicine
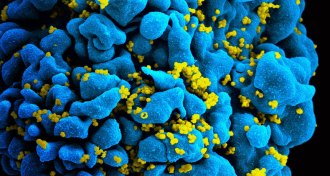
Health & MedicineBy ganging up, HIV antibodies may defeat the virus
A duo or trio of powerful antibodies was effective at stopping an HIV-like infection in lab monkeys, two studies find.
-
 Genetics
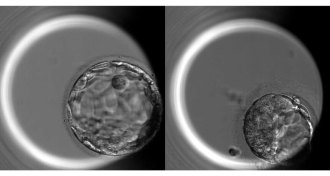
GeneticsIn a first, human embryos edited to explore gene function
In groundbreaking research, CRISPR/Cas9 used to study human development for the first time.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesNow we know how much glacial melting ‘watermelon snow’ can cause
Algae that give snow a red tint are making glacial snow in Alaska melt faster.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsA new test of water ripples supports the idea of quantum heat in a vacuum
Water waves bolster theory that accelerating space travelers really feel the heat.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAnimal goo inspires better glue
Researchers are turning to nature to create adhesives that work in the wet environment of the human body.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyR.I.P. Cassini
After 20 years, nearly 300 orbits and pioneering discoveries, the Cassini spacecraft plunges to its death in Saturn’s atmosphere — taking data until its very last breath.