News
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyNeutron star collision showers the universe with a wealth of discoveries
A collision of neutron stars was spotted with gravitational waves for the first time. Telescopes captured gamma rays, visible light and more from the smashup.
-
 Earth
EarthWhen the Larsen C ice shelf broke, it exposed a hidden world
Scientists plan urgent missions to visit the world the Larsen C iceberg left behind.
-
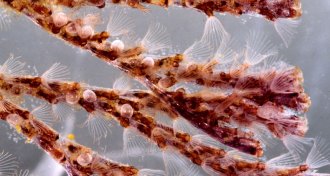 Chemistry
ChemistryA potential drug found in a sea creature can now be made efficiently in the lab
Cooking bryostatin 1 up in a lab lets researchers explore its potential as a drug.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyOddball dwarf planet Haumea has a ring
The dwarf planet Haumea is now the most distant ringed object spotted in the solar system.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyHow to make the cosmic web give up the matter it’s hiding
Half the ordinary matter in the universe is unaccounted for. Astronomers may now have a new way to see it spanning the space between galaxies.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyEconomics Nobel nudges behavioral economist into the limelight
Behavioral economist Richard Thaler started influential investigations of behavioral economics, which earned him the 2017 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences.
By Bruce Bower -
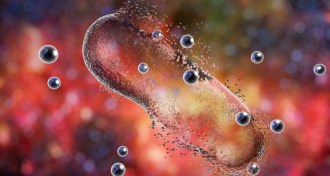 Tech
TechSuperbugs may meet their match in these nanoparticles
Quantum dots and antibiotics hit bacteria with a one-two punch.
-
 Tech
TechNew atomic clock is most precise yet
This next-gen atomic clock ticks at a steady beat, but time will tell just how well it tells time.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureMuch of the world’s honey now contains bee-harming pesticides
A controversial group of chemicals called neonicotinoids has a global impact, tests of honey samples show.
-
 Physics
PhysicsProton size still perplexes despite a new measurement
Study of hydrogen atoms supports the case for a smaller proton.
-
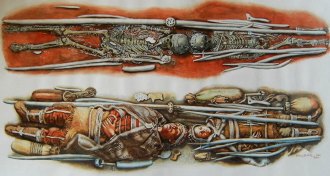 Genetics
GeneticsAncient humans avoided inbreeding by networking
Ancient DNA expands foragers’ social, mating networks.
By Bruce Bower -
 Chemistry
ChemistryChemistry Nobel Prize goes to 3-D snapshots of life’s atomic details
An imaging technique that gives up-close 3-D views of proteins is honored in this year's chemistry Nobel Prize.
By Carolyn Gramling and Laurel Hamers