News
-
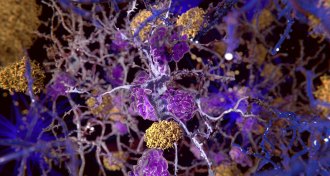 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSpecks in the brain attract Alzheimer’s plaque-forming protein
Globs of an inflammatory protein can spur the formation of amyloid-beta clumps, a study in mice shows.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomySmothered jet may explain weird light from neutron star crash
The neutron star collision whose gravitational waves were detected is still glowing in radio waves. The source of those waves might be a new phenomenon.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe sun’s outer atmosphere is far more complex than previously thought
The outer corona of the sun was thought to be smooth and uniform. New observations show it’s anything but.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSpecialized protein helps these ground squirrels resist the cold
A less active cold-sensing protein explains, in part, why some hibernating ground squirrels are more tolerant of chilly conditions than the animals’ nonhibernating kin.
-
 Physics
PhysicsA new kind of spiral wave embraces disorder
Newly discovered spiral wave chimera is disordered in its center.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyOur first interstellar visitor may be a camouflaged comet
Originally thought to be a rocky asteroid, an interstellar traveler may have a comet’s icy heart.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyAI has found an 8-planet system like ours in Kepler data
An AI spotted an eighth planet circling a distant star, unseating the solar system as the sole record-holder for most known planets.
-
 Climate
ClimateThese weather events turned extreme thanks to human-driven climate change
Ruling out natural variability, scientists say several of 2016’s extreme weather events wouldn’t have happened without human-caused climate change.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceSaturn’s rings are surprisingly young and may be from shredded moons
Final data from the Cassini spacecraft put a date and a mass on the gas giant’s iconic rings.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyU.S. religion is increasingly polarized
Organized religion in the United States increasingly belongs to fervent believers, a new study finds.
By Bruce Bower -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceIn a tally of nerve cells in the outer wrinkles of the brain, a dog wins
Among some carnivores, golden retrievers rate at the top for numbers of nerve cells, study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFracking linked to low birth weight in Pennsylvania babies
Babies born to moms living within one kilometer of a hydraulic fracturing site were more likely to be born underweight, researchers say.