News
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyPollution is endangering the future of astronomy
Astronomers discuss multiple threats from pollution that will make it harder to observe the night sky.
By Dan Garisto -
 Climate
ClimateRising CO2 in lakes could keep water fleas from raising their spiky defenses
Rising CO2 in freshwaters may change how predators and prey interact in lakes.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNot all strep infections are alike and it may have nothing to do with you
Add-on genes in some bacteria shape the way strains interact with the immune system.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyFast radio bursts may be from a neutron star orbiting a black hole
A repeating fast radio burst has twisted waves, suggesting its home has an unusually strong magnetic field.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceThis artificial cartilage gets its strength from the stuff in bulletproof vests
One of the key ingredients in this artificial cartilage is a nanoversion of the synthetic fiber in body armor.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsMagnets with a single pole are still giving physicists the slip
Using data from particle accelerators and dead stars, scientists eliminate some possible masses for magnetic monopoles.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesNew pill tracks gases through your gut
Swallowing these pill-sized sensors could give new insight into what’s going on in your gut.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyWhite dwarf’s inner makeup is mapped for the first time
The first map of the internal composition of a white dwarf star shows these stellar corpses contain more oxygen than expected, challenging stellar evolution theories.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBlowflies use drool to keep their cool
Personal air conditioning the blowfly way: Dangle a droplet of saliva and then reswallow.
By Susan Milius -
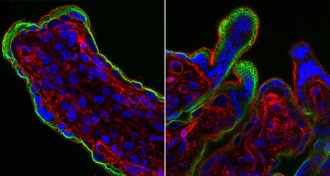 Life
LifeA key virus fighter is implicated in pregnancy woes
In mice, activating a key component of the body’s antiviral machinery in response to a Zika infection can cause harm to developing fetuses.
-
 Anthropology
Anthropology‘Laid-back’ bonobos take a shine to belligerents
Unlike people, these apes gravitate toward those who are unhelpful.
By Bruce Bower -
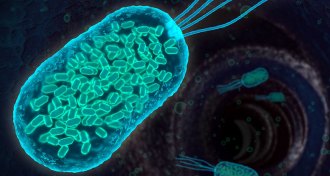 Microbes
MicrobesThese disease-fighting bacteria produce echoes detectable by ultrasound
Ultrasound can help keep tabs on genetically modified bacteria to better fight disease inside the body.