News
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHumans don’t get enough sleep. Just ask other primates.
Short, REM-heavy sleep bouts separate humans from other primates, scientists find. Sleeping on the ground may have a lot to do with it.
By Bruce Bower -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsPollution regulations help Chesapeake Bay seagrass rebound
Regulations that have reduced nitrogen runoff into the Chesapeake Bay are driving the recovery of underwater vegetation.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyMassive stellar flare may have fried Earth’s nearest exoplanet
A massive flare made Proxima Centauri 1,000 times brighter in 10 seconds, dimming hopes that its planet may be habitable.
-
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial IntelligenceIn the future, an AI may diagnose eye problems
Artificial intelligence could help diagnose blinding eye diseases and other illnesses, speeding up medical care in areas where specialists might be scarce.
-
 Physics
PhysicsKnotted structures called skyrmions seem to mimic ball lightning
Skyrmions in a quantum state of matter have something surprising in common with ball lightning — linked magnetic fields.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryExtreme cold is no match for a new battery
A rechargeable battery that works at –70° C could be used in some of the coldest places on Earth or other planets.
-
 Earth
EarthEarly land plants led to the rise of mud
New research suggests early land plants called bryophytes, which include modern mosses, helped shape Earth’s surface by creating clay-rich river deposits.
-
 Animals
AnimalsIt’s official: Termites are just cockroaches with a fancy social life
On their latest master list of arthropods, U.S. entomologists have finally declared termites to be a kind of cockroach.
By Susan Milius -
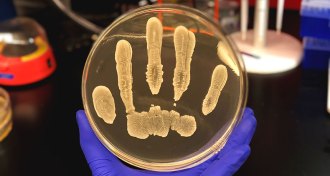 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHuman skin bacteria have cancer-fighting powers
Strains of a bacteria that live on human skin make a compound that suppressed tumor growth in mice.
-
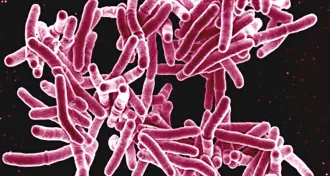 Microbes
MicrobesA new way to make bacteria glow could simplify TB screening
A new dye to stain tuberculosis bacteria in coughed-up mucus and saliva could expedite TB diagnoses and drug-resistance tests.
-
 Cosmology
CosmologyHere’s when the universe’s first stars may have been born
The first stars lit the cosmos by 180 million years after the Big Bang, radio observations suggest.
-
 Life
LifeA rare rainstorm wakes undead microbes in Chile’s Atacama Desert
Microbial life in Chile’s Atacama Desert bursts into bloom when moisture is available.