News
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow honeybees’ royal jelly might be baby glue, too
A last-minute pH shift thickens royal jelly enough to stick queen larvae to the ceiling of hive cells.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe science behind cancer warnings on coffee is murky at best
The risks of acrylamide in coffee are not as clear as a California court ruling may suggest.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceEggshell nanostructure protects a chick and helps it hatch
The nanoscale structure of a chicken eggshell changes to fulfill different functions as the egg incubates.
-
 Animals
AnimalsToxins from the world’s longest animal can kill cockroaches
Bootlace worms can stretch up to 55 meters long and ooze toxins that can kill cockroaches and green crabs.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsSome frogs may be bouncing back after killer chytrid fungus
Frogs in Panama may be developing defenses against a fatal skin disease, a new study suggests.
By Susan Milius -
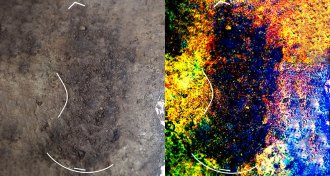 Archaeology
ArchaeologyFootprints put people on Canada’s west coast 13,000 years ago
Island tracks indicate early New World settlers traveled down the North American Pacific coast about 13,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Astronomy
AstronomyDark matter is MIA in this strange galaxy
A galaxy without dark matter bolsters the case that the invisible substance really exists.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineKid-friendly e-cigarette ads appear to work
Teens who hadn’t used tobacco products but were receptive to e-cigarettes ads were more likely to try vaping or smoking.
-
 Earth
EarthPowerful New England quake recorded in pond mud
The newfound sediment signature of the 1755 Cape Ann earthquake could be used to trace other prehistoric temblors.
-
 Life
Life‘Nanobot’ viruses tag and round up bacteria in food and water
Viruses called phages evolved to hunt bacteria. With magnetic nanoparticles and genetic engineering, they become nanobots that work for us.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceWater may have killed Mars’ magnetic field
Extra hydrogen near the Red Planet’s iron core could have shut down convection.
-
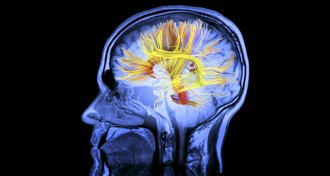 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWhen tickling the brain to stimulate memory, location matters
Conflicting results regarding the benefits of brain stimulation may be explained by the precise location of electrodes.