News
-
 Tech
TechThe Facebook data debacle may not change internet behavior
In the wake of the Facebook data breach, personal privacy experts say there’s little individuals can do to control their personal information online.
-
 Climate
ClimateCargo ships must cut their emissions in half by 2050
A new international agreement places a cap on greenhouse gas emissions from international cargo ships.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyTales of rampant suicide among Custer’s soldiers may be overblown
Few of Custer’s men killed themselves in the face of overwhelming Native American numbers at the Battle of the Little Bighorn, skeletal data suggest.
By Bruce Bower -
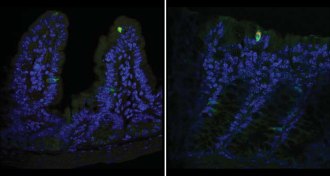 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis is how norovirus invades the body
Norovirus targets a rare type of gut cell, a study in mice finds.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsSweet potatoes might have arrived in Polynesia long before humans
Genetic analysis suggests that sweet potatoes were present in Polynesia over 100,000 years ago, and didn’t need help crossing the Pacific.
By Dan Garisto -
 Astronomy
AstronomyWith the launch of TESS, NASA will boost its search for exoplanets
The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite will set the stage for the next chapter of exoplanet exploration.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyColorful moth wings date back to the dinosaur era
Microscopic structures that scatter light to give color to the wings of modern butterflies and moths date back almost 200 million years.
-
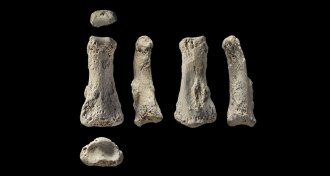 Anthropology
AnthropologyFinger fossil puts people in Arabia at least 86,000 years ago
A desert discovery suggests that Arabia was an ancient human destination.
By Bruce Bower -
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsThe search for mysterious dark matter underdogs steps up
Dark matter particles called axions are finally being put to the test.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentMicroplastics may enter freshwater and soil via compost
Compost is pinpointed as a source of plastic pollution, but environmental fate and effects unknown.
-
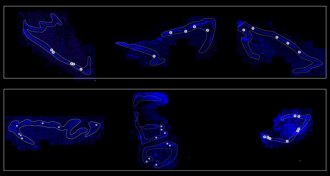 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHuman brains make new nerve cells — and lots of them — well into old age
In humans, new neurons are still born in old brains, new research suggests.
-
 Earth
EarthEfforts to contain Mississippi floods may have made them worse
Intensive management of the Mississippi River has increased the size of its largest floods, suggests a new study.