News
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyClues to an Iron Age massacre lie in what the assailants left behind
Ancient Scandinavian massacre may reflect power struggles after Rome’s fall.
By Bruce Bower -
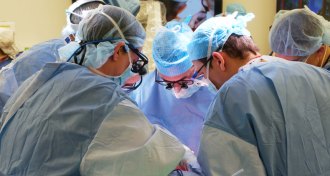 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe first penis-scrotum transplant is the latest to go beyond lifesaving
Advances that give patients new faces, hands and more aim to improve quality of life
-
 Climate
ClimateHeat waves are roasting reefs, but some corals may be resilient
The latest research on coral reefs clarifies the devastation of heat waves and looks at how coral might be able to adapt to warming waters.
By Dan Garisto -
 Climate
ClimateRising CO2 levels might not be as good for plants as we thought
A 20-year experiment spots a reversal in the way two kinds of plants take up extra carbon from the atmosphere.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceThis meteorite’s diamonds hint that it was born in a lost planet
Bits of metal nestled inside diamonds suggest the space rock could have formed in a Mars-sized protoplanet in the early solar system.
-
 Tech
TechWhy touch can be such a creepy sensation in VR
Touch sensation in VR can go from immersive to unnerving as the feeling gets more realistic, if you can’t see the source.
-
 Oceans
OceansMasses of shrimp and krill may play a huge role in mixing oceans
Hoards of migrating shrimp and krill can cause large-scale turbulence in the ocean, a new study suggests.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThese seals haven’t lost their land ancestors’ hunting ways
Clawed pawlike forelimbs help true seals hunt like their land-dwelling ancestors.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyThis ancient Maya city may have helped the Snake King dynasty spread
A rural hub in an ancient Maya state gets its due with some laser help.
By Bruce Bower -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyHere’s why putting a missile defense system in space could be a bad idea
Expanding missile defense capabilities could put the world on a slippery slope to space warfare.
-
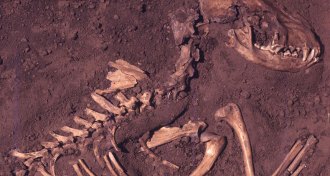 Archaeology
ArchaeologyDogs lived and died with humans 10,000 years ago in the Americas
Dogs unearthed at sites in Illinois were older than originally thought.
By Bruce Bower -
 Space
SpaceLasers squeezed iron to mimic the conditions of exoplanet cores
In the first experiment to measure what exoplanets might be like on the inside, scientists hit iron with 176 lasers at once.