News
-
 Life
LifeThere’s a genetic explanation for why warmer nests turn turtles female
Scientists have found a temperature-responsive gene that controls young turtles’ sex fate.
-
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial IntelligenceThis AI uses the same kind of brain wiring as mammals to navigate
This AI creates mental maps of its environment much like mammals do.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyGaia delivers a trove of data revealing secrets of the Milky Way
Astronomers are already using Gaia’s new information to estimate the galaxy’s mass, the diameter of exoplanets and more.
-
 Earth
EarthHow long will Kilauea’s eruption last?
A volcanologist with the U.S. Geological Survey answers burning questions about the ongoing Kilauea eruption.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyNew ideas about how stars die help solve a decades-old mystery
New ideas about stellar evolution help explain why astronomers see so many bright planetary nebulae where they ought not be.
-
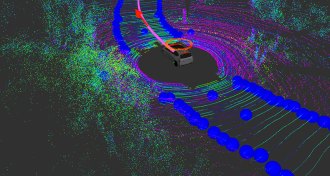 Tech
TechThis self-driving car could one day take you on a real road trip
Most autonomous cars are city drivers. This one’s made for cross-country road trips.
-
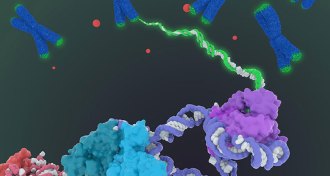 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAn enzyme involved in cancer and aging gets a close-up
The structure of telomerase, described with the greatest detail yet, may give researchers clues to cancer treatments and other telomerase-related illnesses.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsAdapting to life in the north may have been a real headache
A cold-sensing protein has adapted to different local climates, also affecting risk of migraine.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceNASA gets ready to launch the first lander to investigate Mars’ insides
The InSight lander is launching to Mars on May 5 and is expected to be in position to sense seismic activity by early 2019.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFDA approves the first smallpox treatment
Concerns about bioterrorism fueled the development of the first treatment for smallpox.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThis ancient fowl bit like a dinosaur and pecked like a bird
A new fossil of Ichthyornis dispar helped scientists create a 3-D reconstruction of the ancient bird’s skull, shedding light on early bird evolution.
-
 Climate
ClimateBull sharks and bottlenose dolphins are moving north as the ocean warms
Rising temperatures are making ocean waters farther north more hospitable for a variety of marine species.