News
-
 Paleontology
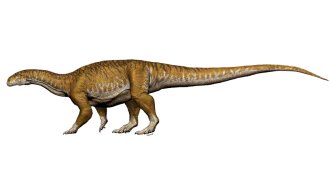
PaleontologyLong-necked dinosaurs grew to be giants in more ways than one
Some early relatives of giant, long-necked sauropods may have used a different strategy to grow to colossal sizes than previously thought.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceDesigner diamonds could one day help build a quantum internet
A new design in artificial diamonds stores and releases quantum information better than others.
-
 Earth
EarthKilauea’s spectacular pyrotechnics show no signs of stopping
Watch some of the most striking videos and images of the strange, fiery beauty of the Hawaii volcano’s ongoing eruption.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSoaring spiders may get cues from electric charges in the air
Spiders can sense atmospheric electric fields, which might give them cues to take to the air.
-
 Neuroscience
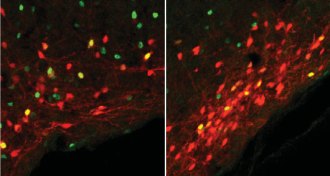
NeuroscienceNerve cells that help control hunger have been ID’d in mice
A mysterious bump on the human brain may be able to dial appetite up or down.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyNASA’s Parker probe is about to get up close and personal with the sun
The Parker Solar Probe is about to make a historic voyage to touch the sun.
-
 Anthropology
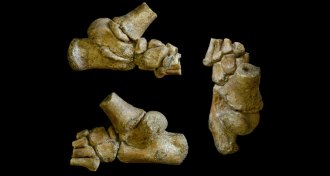
AnthropologyFoot fossil pegs hominid kids as upright walkers 3.3 million years ago
A foot from an ancient hominid child suggests that Lucy’s species, Australopithecus afarensis, walked early in life.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsResearchers create hybrid embryos of endangered white rhinos
Scientists have made the first rhino embryos, providing a small glimmer of hope for the nearly extinct northern white rhinoceros.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEvidence grows that an HPV screen beats a Pap test at preventing cancer
More research finds that a test for human papillomavirus infection catches precancerous cervical cells better than the standard test, a Pap.
-
 Life
LifeThis ‘junk’ gene may be important in embryo development
Mice — and maybe humans — can’t get past the two-cell stage of development without a particular type of jumping gene.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsKoala genome may contain clues for helping the species survive
The complete genetic instruction book of a koala may explain why the cuddly-looking cuties are such picky eaters, among other secrets.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsMini machines can evade friction by taking quantum shortcuts
Special maneuvers allow researchers to create tiny machines that are as efficient as possible.