News
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis tick may play a part in gumming up your arteries
Having antibodies to a sugar tied to red-meat allergy is associated with more plaque in the artery walls, a small study shows.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHow an ancient stone money system works like cryptocurrency
Money has ancient and mysterious pedigrees that go way beyond coins.
By Bruce Bower -
 Microbes
MicrobesHow a slime mold near death packs bacteria to feed the next generation
Social amoebas that farm bacteria for food use proteins to preserve the crop for their offspring.
By Susan Milius -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceWhat does Mars’ lake mean for the search for life on the Red Planet?
A lake spotted hiding under Martian ice could support life, but finding out if anything lives there could be challenging.
-
 Physics
PhysicsA star orbiting a black hole shows Einstein got gravity right — again
For the first time, general relativity has been confirmed in the region near a supermassive black hole.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHere’s why wounds heal faster in the mouth than in other skin
Wounds in the mouth heal speedily thanks to some master regulators of immune reactions.
-
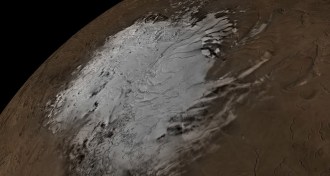 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMars (probably) has a lake of liquid water
A 15-year-old Mars orbiter has spotted signs of a salty lake beneath the Red Planet’s south polar ice sheets.
-
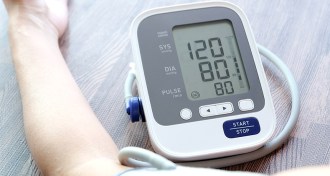 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLowering blood pressure may help the brain
Aggressively treating high blood pressure had a modest positive effect on the development of an early form of memory loss.
-
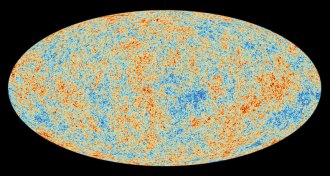 Physics
PhysicsThe Planck satellite’s picture of the infant universe gets its last tweaks
Scientists have released the last big result from the cosmic microwave background experiment Planck.
-
 Tech
TechA new kind of spray is loaded with microscopic electronic sensors
For the first time, researchers have built circuits on microscopic chips that can be mixed into an aerosol spray.
-
 Oceans
OceansShallow reef species may not find refuge in deeper water habitats
Coral reefs in deep-water ecosystems may not make good homes for species from damaged shallow reefs.
-
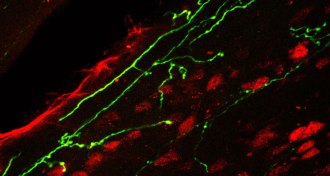 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow a variation on Botox could be used to treat pain
Drugs that incorporate modified botulinum toxin provide long-term pain relief, a study in mice finds.