News
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLyme and other tickborne diseases are on the rise in the U.S. Here’s what that means.
A record number of tickborne diseases were reported in the United States in 2017. An infectious disease physician discusses that result and others.
-
 Climate
ClimateDevelopment near natural areas puts more Californians in the path of wildfires
As urbanization extends its reach into once-natural areas, more homes and people are at risk from wildfires.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsCoffee or tea? Your preference may be written in your DNA
Coffee or tea is a bitter choice, a taste genetics study suggests.
-
 Earth
EarthA massive crater hides beneath Greenland’s ice
The discovery of a vast crater in Greenland suggests that a 1-kilometer-wide asteroid hit the Earth between 2.6 million and 11,700 years ago.
-
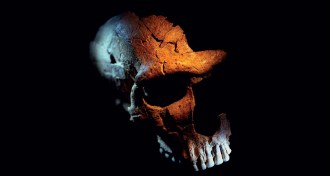 Anthropology
AnthropologySkull damage suggests Neandertals led no more violent lives than humans
Neandertals’ skulls suggest they didn’t lead especially injury-prone lives.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsSound-absorbent wings and fur help some moths evade bats
Tiny ultrathin scales on some moth wings absorb sound waves sent out by bats on the hunt.
-
 Animals
AnimalsClimate change may have made the Arctic deadlier for baby shorebirds
What were once relatively safe havens in the Arctic are now feasting sites for predators of baby birds.
By Susan Milius -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceChina is about to visit uncharted territory on the moon
The next two Chinese missions to the moon will visit places no spacecraft has been before. The rest of the world wants a piece of the lunar action.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA potent fish oil drug may protect high-risk patients against heart attacks
People with, or at high risk of, cardiovascular disease lowered their chances of having a heart attack or stroke with a drug containing an omega-3 fatty acid.
-
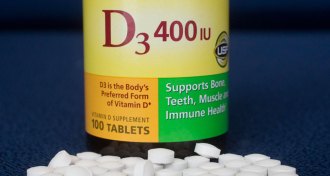 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVitamin D supplements don’t prevent heart disease or cancer
Vitamin D supplements won’t cut your risk of heart attack or stroke, according to highly anticipated study results.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsAncient DNA suggests people settled South America in at least 3 waves
Genetic studies of ancient remains are filling in the picture of who the earliest Americans were and how they spread through the Americas long ago.
-
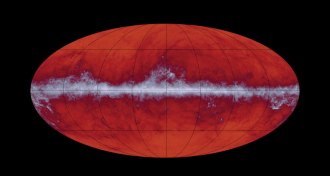 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceHints of Oort clouds around other stars may lurk in the universe’s first light
Sifting through the universe’s early light could reveal planetary graveyards orbiting other stars.