News
-
 Animals
AnimalsVaccines may help bats fight white nose syndrome
Researchers are developing an oral vaccine that helps little brown bats survive the fungal disease white nose syndrome.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDoes eating ultraprocessed food affect weight gain? It’s complicated
Laying off ultraprocessed foods and switching to whole foods may help some people manage their weight, a small study finds.
-
 Life
LifeBloodthirsty bedbugs have feasted on prey for 100 million years
Research sheds light on the evolutionary history of the bloodsucking bedbugs. The first species evolved at least as early as the Cretaceous, scientists say.
-
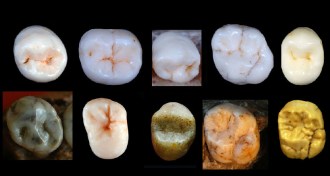 Anthropology
AnthropologyFossil teeth push the human-Neandertal split back to about 1 million years ago
A study of fossilized teeth shifts the age of the last common ancestor between Neandertals and humans.
By Bruce Bower -
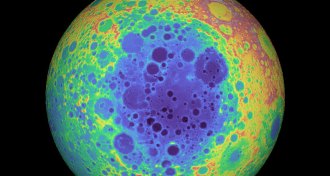 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceChina’s lunar rover may have found minerals from the moon’s mantle
The Chang’e-4 mission spotted material on the lunar surface that appears to contain bits originating from the moon’s interior.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsTweaking one gene with CRISPR switched the way a snail shell spirals
The first gene-edited snails confirm which gene is responsible for the direction of the shell’s spiral.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceApollo-era moonquakes reveal that the moon may be tectonically active
Moonquakes recorded decades ago suggest the moon is tectonically active. Knowing more about that activity could help scientists identify where to land future spacecraft.
-
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial IntelligenceA new AI acquired humanlike ‘number sense’ on its own
A new artificial intelligence seems to share our intuitive ability to estimate numbers at a glance.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDeep-sea fishes’ eye chemistry might let them see colors in near darkness
An unexpected abundance of proteins for catching dim light evolved independently in three groups of weird deep-sea fishes.
By Susan Milius -
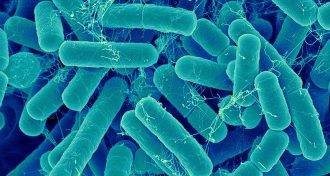 Life
LifeA gut bacteria transplant may not help you lose weight
A small study finds that transplanting gut microbes from a lean person into obese people didn’t lead to weight loss, as hoped.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyDying stars called collapsars may forge much of the universe’s gold
Spinning stars that collapse into black holes could help explain the origins of heavy elements such as gold and silver.
-
 Physics
PhysicsWhat a nearby kilonova would look like
Physicists imagined what we’d see in the sky if two neutron stars collided just 1,000 light-years from Earth.