News
-
 Health & Medicine
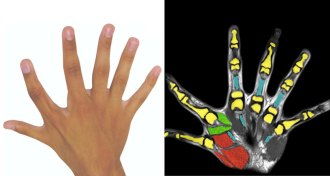
Health & MedicineExtra fingers, often seen as useless, can offer major dexterity advantages
Two people born with six fingers on each hand can control the extra digit, using it to do tasks better than five-fingered hands, a study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA tiny crater on viruses behind the common cold may be their Achilles’ heel
Researchers have discovered a potential new drug target in a family of viruses responsible for the common cold and more serious infections.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyThese knotted cords may hide the first evidence that the Incas collected taxes
Some knotted string devices point to crop levies imposed by the Incan empire, researchers say. But other khipus continue to evade description.
By Bruce Bower -
 Genetics
GeneticsGenealogy companies could struggle to keep clients’ data from police
Police probably won’t stop searching DNA family trees to find crime suspects. New restrictions on database searches could spur more fights over privacy.
-
 Life
LifeSome fungi trade phosphorus with plants like savvy stockbrokers
New views show how fungi shift their stores of phosphorus toward more favorable markets where the nutrient is scarce.
By Susan Milius -
 Astronomy
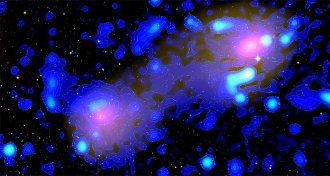
AstronomyIn a first, magnetic fields have been spotted between two galaxy clusters
The discovery of magnetic fields in the gaseous filament between two galaxy clusters suggests that some large cosmic structures are magnetized.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWorms lure two new species of hopping rats out of obscurity
In the Philippines, scientists have identified two new species of shrew-rat, an animal whose limited habitat plays host to remarkable biodiversity.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLimiting global warming to 1.5 degrees C could prevent thousands of deaths in the U.S.
A study projecting heat-related mortality in 15 U.S. cities illustrates urban risk from global warming.
-
 Earth
EarthSoil eroded by glaciers may have kick-started plate tectonics
How plate tectonics got going is a mystery. Now scientists say they’ve found a key part of the story: massive piles of sediment dumped in the ocean.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe accretion disk around our galaxy’s black hole has been spotted at last
The Milky Way's central black hole has a disk of gas and dust orbiting it, astronomers can finally say with confidence.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentChemicals in biodegradable food containers can leach into compost
PFAS compounds from compostable food containers could end being absorbed by plants and later eaten by people, though the health effects are unclear.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA new experiment didn’t find signs of dreaming in brain waves
Brain activity that powers dreams may reveal crucial insight into consciousness, but a new study failed to spot evidence of the neural flickers.