News
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA mouse’s metabolism may follow circadian rhythms set by gut bacteria
While animals’ circadian clocks control functions from sleep to hormone release, gut bacteria dictate when mice’s small intestines take up fat.
-
 Space
SpaceThis fast radio burst shined a light on a galaxy’s mysterious gas halo
A lucky alignment let astronomers probe one galaxy’s diffuse gas using a brief, bright blast from a more distant galaxy.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRockland’s measles outbreak is over, but U.S. elimination status is still at risk
Officials in Rockland County in New York announced that their measles outbreak, which began October 1 of last year, is finally finished.
-
 Life
LifeLosing genes may have helped whales’ ancestors adapt to life under the sea
Jettisoning genes tied to saliva and the lungs, among others, could have smoothed ancient cetaceans’ land-to-water transition 50 million years ago.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyBaby bottles may go back millennia in Europe
Europe’s early farmers used spouted vessels to wean infants, an analysis of residue from animal milk left in the containers suggests.
By Bruce Bower -
 Climate
ClimateIPCC report warns of a bleak future for oceans and frozen regions under climate change
A new IPCC report offers dire warnings about how climate change is altering oceans, the polar regions and the high snowy mountains.
-
 Climate
ClimateHow climate change is already altering oceans and ice, and what’s to come
A new IPCC report gives the lowdown on how climate change is already wreaking havoc on Earth’s oceans and frozen regions, and how much worse things could get.
-
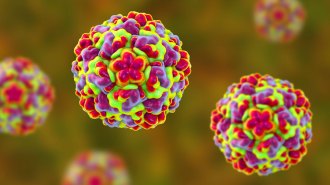 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDisabling one protein might one day lead to a cure for the common cold
Scientists have identified a protein in humans that some viruses, including those that cause colds, need to spread.
By Sofie Bates -
 Life
LifeCats may have ‘attachment styles’ that mirror people’s
In a new study, 65 percent of felines formed secure attachments with their owners. Like people, other cats were ambivalent or avoidant.
By Sofie Bates -
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsRumors hint that Google has accomplished quantum supremacy
Reports suggest a quantum computer has bested standard computers on one type of calculation, but practical applications are still a distant goal.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceIndia’s first attempt to land on the moon appears to have failed
Indian scientists haven’t heard from the Vikram lander for a full lunar day, after they lost contact during the robotic spacecraft’s descent.
-
 Life
LifeWe’ve lost 3 billion birds since 1970 in North America
Scientists estimated the change in total number of individual birds since 1970. They found profound losses spread among rare and common birds alike.