News
-
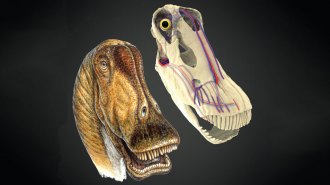 Paleontology
PaleontologyBig dinosaurs kept cool thanks to blood vessel clusters in their heads
Giant dinosaurs evolved several strategies for cooling their blood and avoiding heatstroke.
-
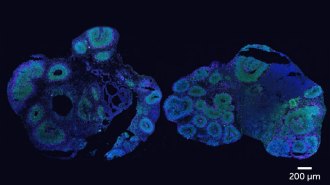 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceOrganoids offer clues to how brains are made in humans and chimpanzees
Three-dimensional clumps of brain cells offer clues about how brains get made in humans and chimpanzees.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA precision drug for prostate cancer may slow the disease’s spread
The drug olaparib could be used to treat men with certain genetic mutations and severe types of prostate cancer, a clinical trial finds.
By Sofie Bates -
 Animals
AnimalsHumpback whales use their flippers and bubble ‘nets’ to catch fish
A study reveals new details of how humpback whales hunt using their flippers and a whirl of bubbles to capture fish.
By Sofie Bates -
 Life
LifeExtreme snowfall kept most plants and animals in one Arctic ecosystem from reproducing
A very snowy winter in 2018 left parts of Greenland covered well into the summer, causing an ecosystem-wide reproductive collapse in one area.
-
 Physics
PhysicsPhysicists have found quasiparticles that mimic hypothetical dark matter axions
These subatomic particles could make up dark matter in the cosmos. A mathematically similar phenomenon occurs in a solid material.
-
 Space
SpaceHow the second known interstellar visitor makes ‘Oumuamua seem even odder
With its gaseous halo and tail, the second discovered interstellar object, 2I/Borisov, looks basically like your run-of-the-mill solar system comet.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyEconomics Nobel goes to poverty-fighting science
Three scientists share the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for developing real-world interventions for tackling poverty.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNearly 1,300 injuries and 29 deaths in the U.S. have been tied to vaping
As the investigation continues, health officials expect multiple causes will be behind the ever-growing number of vaping-related lung injuries.
-
 Space
SpaceA supermassive black hole shredded a star and was caught in the act
Astronomers have gotten the earliest glimpse yet of a black hole ripping up a star, a process known as a tidal disruption event.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceA new cooling technique relies on untwisting coiled fibers
A “twist fridge” operates via twistocaloric cooling, a technique that generates cooling by unraveling twisted strands.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAncient European households combined the rich and poor
Homes combined “haves” and “have-nots” in a male-run system, suggests a study that challenges traditional views of ancient social stratification.
By Bruce Bower