News
-
 Humans
HumansAn ancient outbreak of bubonic plague may have been exaggerated
Archaeological evidence suggests that an epidemic that occurred several centuries before the Black Death didn’t radically change European history.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeA tree in Brazil’s arid northeast rains nectar from its flowers
Northeast Brazil is home to a tree that entices bat pollinators by making a “sweet rain” of nectar.
By Jake Buehler -
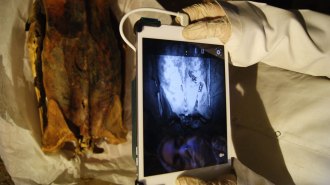 Archaeology
ArchaeologyInfrared images reveal hidden tattoos on Egyptian mummies
Infrared images show a range of markings on seven female mummies, raising questions about ancient Egyptian tattoo traditions.
By Bruce Bower -
 Space
SpaceA newfound black hole in the Milky Way is weirdly heavy
A dark mass about 68 times as massive as the sun is locked in orbit with a star in our galaxy. Theory says that such black holes shouldn’t get so big.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsA new, theoretical type of time crystal could run without outside help
The idea tiptoes closer to the original concept of time crystals, first proposed in 2012.
-
 Humans
HumansArchaeologists tie ancient bones to a revolt chronicled on the Rosetta Stone
The skeleton of an ancient soldier found in the Nile Delta provides a rare glimpse into an uprising around 2,200 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Climate
ClimateCountries urgently need to ramp up emissions cuts to meet climate targets
A new U.N. report finds that pledged emissions cuts aren’t nearly enough to limit warming to “well below” 2 degrees Celsius by 2100.
-
 Earth
EarthCritics say an EPA rule may restrict science used for public health regulations
Editors of six major scientific journals argue that a rule proposed by the U.S. EPA may keep key data from factoring into environmental regulations.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA dose of ketamine could lessen the lure of alcohol
Ketamine may weaken wobbly memories of drinking, a trick that might ultimately be useful for treating alcohol addiction.
-
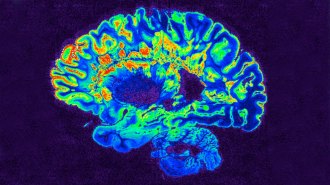 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA protein helps disease-causing immune cells invade MS patients’ brains
Blocking the protein may hinder B cells invading the brain in multiple sclerosis, a study in mice and ‘stand-in’ human brain barriers finds.
By Sofie Bates -
 Climate
ClimateMost Americans now see signs of climate change where they live
In a Pew Research survey, most Americans said the U.S. government isn’t doing enough to counter climate change amid local weather extremes.
-
 Astronomy
Astronomy19 more galaxies mysteriously missing dark matter have been found
The finding reveals a population of dwarf galaxies that defy common wisdom about how these star systems form and evolve.