News
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyLicelike insects munched on dinosaur feathers around 100 million years ago
Fossils in amber push the origin of feather-feeding insects back over 50 million years, a study finds.
By Sofie Bates -
 Climate
ClimateSee how an Alaskan glacier has shrunk over time
Scientists have created a time-lapse series of images of the retreat of an Alaskan glacier using NASA and U.S. Geological Survey Landsat data.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsA newly found Atacama Desert soil community survives on sips of fog
Lichens and other fungi and algae unite to form “grit-crust” on the dry soil of Chile’s Atacama Desert and survive on moisture from coastal fog.
By Jack J. Lee -
 Space
SpaceElectric charges on dust grains may help explain how planets are born
In an experiment, glass beads clung together like protoplanetary dust particles when shaken and flung more than 100 meters skyward.
-
 Oceans
OceansStealthy robots with microphones could improve maps of ocean noise
Recordings from underwater microphones on stealthy robotic gliders could create a better “soundscape” of noises throughout the ocean, researchers say.
By Sofie Bates -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyWhy Rembrandt and da Vinci may have painted themselves with skewed eyes
A strongly dominant eye, not an eye disorder, may explain why some great artists painted themselves with one eye turned outward.
By Sofie Bates -
 Life
LifeAn ancient critter may shed light on when mammals’ middle ear evolved
Rare skeletons are helping to pin down the evolution of mammals’ three middle ear bones, known popularly as the hammer, anvil and stirrup.
-
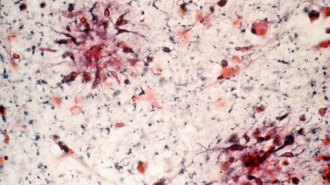 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA once-scrapped Alzheimer’s drug may work after all, new analyses suggest
An antibody that targets Alzheimer’s sticky protein amyloid showed promise in slowing mental decline, according to the company that’s developing it.
-
 Life
LifeA single-celled protist reacts to threats in surprisingly complex ways
New research validates a century-old experiment that shows single-celled organisms are capable of complex “decision making.”
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists’ brains shrank a bit after an extended stay in Antarctica
The experience of an isolated, long-term mission at an Antarctic research station slightly shrunk a part of crew members’ brains, a small study finds.
-
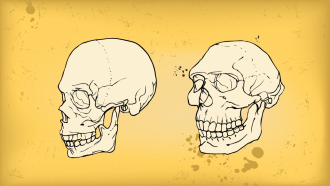 Humans
HumansA gene tied to facial development hints humans domesticated themselves
Scientists may have identified a gene that ties together ideas about human evolution and animal domestication.
-
 Space
SpaceNASA’s Parker probe reveals the sun’s rogue plasma waves and magnetic islands
Scientists have analyzed the Parker probe’s first data, giving a peek at what’s to come as the craft moves closer to the sun over the next few years.