News
-
 Physics
PhysicsThis fundamental constant of nature remains the same even near a black hole
A number that sets the strength of electromagnetic interactions isn’t altered by the extreme gravity around the Milky Way’s supermassive black hole.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTo tackle the new coronavirus, scientists are accelerating the vaccine process
Scientists are turning to nontraditional approaches to create vaccines and therapeutics that target the novel coronavirus.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineU.S. drug deaths dipped in 2018, but cocaine and meth overdoses rose
In 2018, the rates of drug overdose deaths for methamphetamine and cocaine surpassed that of prescription opioids.
-
 Climate
ClimateEconomic costs of rising seas will be steeper than we thought, unless we prepare
A study estimates 4 percent in annual global GDP losses by 2100 due to sea level rise, unless people curb emissions and prepare for flood risks.
By Megan Sever -
 Humans
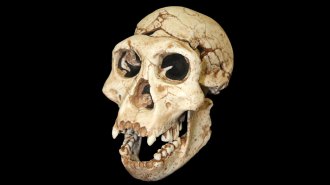
HumansThe earliest known hominid interbreeding occurred 700,000 years ago
The migration of Neandertal-Denisovan ancestors to Eurasia some 700,000 years ago heralded hookups with a resident hominid population.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
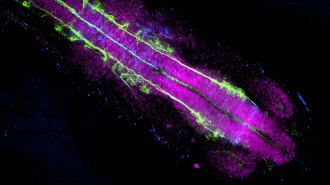
LifeHow African turquoise killifish press the pause button on aging
The fish’s embryos can enter a state of suspended growth to survive dry spells. A study shows that state protects them from aging, and hints at how.
-
 Climate
ClimateClimate change is slowly drying up the Colorado River
Annual water flow in the Colorado River decreased by over 11 percent due to warming in the 20th century, a new study estimates.
-
 Life
LifeA new lizard parasite is the first known to move from mom to baby
Nematodes were found living in a lizard’s ovaries and the braincase of her embryos — the first evidence of a reptile parasite that jumps generations.
By Pratik Pawar -
 Climate
ClimateFossil fuel use may emit 40 percent more methane than we thought
Ice cores suggest natural seeps release less methane than was estimated, meaning industry produces nearly all of today’s geologic methane emissions.
-
 Archaeology
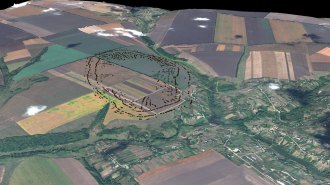
ArchaeologyAncient ‘megasites’ may reshape the history of the first cities
At least two ancient paths to urban development existed, some archaeologists argue.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsOne blind, aquatic salamander may have sat mostly still for seven years
Olms may live for about century and appear to spend their time moving sparingly.
By Jake Buehler -
 Astronomy
AstronomyMolecular oxygen has been spotted beyond the Milky Way for the first time
Astronomers have detected molecular oxygen in another galaxy for the first time. The discovery is only the third sighting beyond our solar system.
By Ken Croswell