News
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryHow to brew a better espresso, according to science
To make more consistent and affordable espresso shots, use fewer beans and grind them more coarsely, a new study says.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyA squid fossil offers a rare record of pterosaur feeding behavior
150 million years ago, a pterosaur attempted to snatch a squid from the ocean surface and lost a tooth in the process.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow the new coronavirus stacks up against SARS and MERS
Coronaviruses are a diverse family that may be becoming more threatening to people.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLevels of certain proteins in the blood may act as concussion biomarkers
College athletes who suffered concussions had elevated blood levels of three proteins, a potential chemical sign that one day may aid diagnosis.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNo, snakes probably aren’t the source of that new coronavirus in China
Scientists are skeptical about a new study that pinpoints snakes as the animal reservoir for the ongoing coronavirus outbreak in China.
-
 Physics
PhysicsA quantum strategy could verify the solutions to unsolvable problems — in theory
A quantum technique for verifying solutions to difficult problems could apply to an “unbelievably huge” class of puzzles.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWHO says China’s coronavirus outbreak isn’t a global emergency yet
While the WHO says the coronavirus outbreak isn’t a global emergency, China has locked down several large cities to stop the virus from spreading.
-
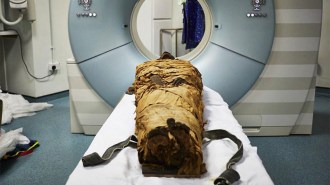 Archaeology
ArchaeologyA 3-D printed vocal tract lets an ancient mummy speak from beyond the grave
A re-created version of a mummy’s vocal tract reveals what this ancient Egyptian might have sounded like.
-
 Life
LifeSparkly exoskeletons may help camouflage beetles from predators
Iridescence, normally thought to help insects stand out, can also camouflage beetles from predators, according to new experimental evidence.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyMount Vesuvius may have suffocated, not vaporized, some victims
A new study suggests people living near Pompeii who hid in stone boathouses died a slower death when the volcano erupted in A.D. 79.
-
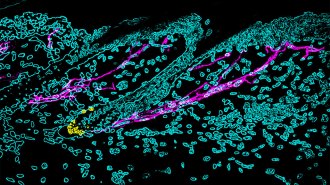 Humans
HumansStress turns hair gray by triggering the body’s fight-or-flight response
A study in mice finds stress responses deplete cells that give hair its pigment, making the strand white.
-
 Earth
EarthFed by human-caused erosion, many river deltas are growing
Deforestation and river damming are changing the shape of river deltas around the globe.