News
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYou can help fight the coronavirus. All you need is a computer
With Folding@home, people can donate computing time on their home computers to the search for a chemical Achilles’ heel in the coronavirus.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhen will the coronavirus pandemic and social distancing end?
Social distancing may have to continue for months to prevent a resurgence of COVID-19. Wider testing and isolation of cases could ease such measures.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe number of steps per day, not speed, is linked to mortality rate
Researchers report an association between the total number of steps a person takes each day and the rate of death from any cause.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsParticles called axions could reveal how matter conquered the universe
Axions, if they exist, may solve not one, not two, but three pressing puzzles of particle physics.
-
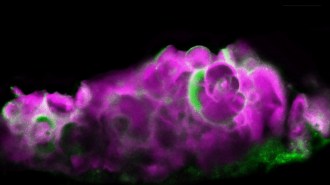 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA tooth-enamel protein is found in eyes with a common form of macular degeneration
Researchers linked a tooth-enamel protein with calcium deposits in eyes suffering ‘dry’ AMD, which could lead to treatments for the vision disorder.
By Alex Fox -
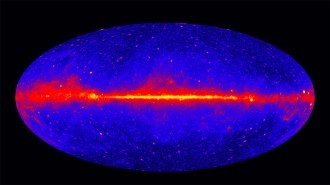 Space
SpaceAstronomers have found the edge of the Milky Way at last
Computer simulations and observations of nearby galaxies let astrophysicists put a firm number on the Milky Way's size.
By Ken Croswell -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy some heart patients may be especially vulnerable to COVID-19
Researchers don’t yet know if the way the coronavirus enters cells may have something to do with the risks to the heart.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyThe Nazareth Inscription’s origins may refute ties to Jesus’ resurrection
Chemical analysis shows the tablet’s marble came from a Greek island, challenging the idea the decree concerned early Christianity in the Middle East.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYoung adults can face severe cases of COVID-19, too
While risk of having a severe case of COVID-19 rises with age, younger adults are also landing in the hospital and ICU, new U.S. statistics show.
-
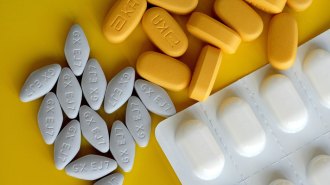 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHIV drugs didn’t work as a coronavirus treatment in a clinical trial
Antiviral HIV drugs “showed no benefit” when given to patients severely ill with COVID-19.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow parents and kids can stay safe and sane during the coronavirus pandemic
Infectious disease experts weigh in on playdates, playgrounds and other parenting questions.
By Laura Sanders and Sujata Gupta -
 Environment
EnvironmentLegos may take hundreds of years to break down in the ocean
Sturdy types of plastic may persist in seawater for much long than scientists previously thought.