News
-
 Paleontology
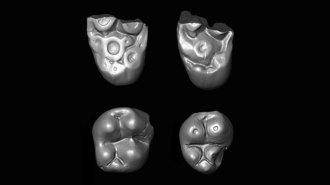
PaleontologyTwo primate lineages crossed the Atlantic millions of years ago
Peruvian primate fossils point to a second ocean crossing by a now-extinct group roughly 35 million to 32 million years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Physics
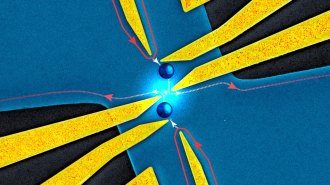
PhysicsCollisions reveal new evidence of ‘anyon’ quasiparticles’ existence
Scientists report evidence that a class of particle called an anyon appears in two-dimensional materials.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWarm weather probably won’t slow COVID-19 transmission much
While some evidence has suggested higher temperatures can affect coronavirus transmission, summer’s arrival probably won’t curb the pandemic much.
-
 Archaeology
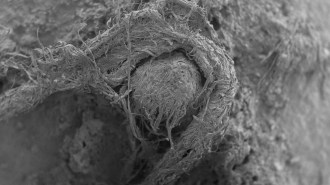
ArchaeologyThis is the oldest known string. It was made by a Neandertal
A cord fragment found clinging to a Neandertal’s stone tool is evidence that our close evolutionary relatives were string makers, too, scientists say.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsHitchhiking oxpeckers warn endangered rhinos when people are nearby
Red-billed oxpeckers do more than just eat parasites from rhinos’ backs. The birds can alert the hunted mammals to potential danger, a study finds.
-
 Space
SpaceNew search methods are ramping up the hunt for alien intelligence
Six decades of radio silence hasn’t stopped scientists searching for intelligent life beyond Earth. In fact, new technologies are boosting efforts.
-
 Climate
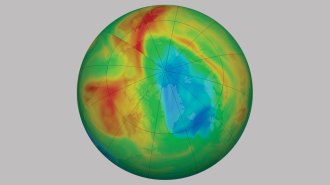
ClimateThe largest Arctic ozone hole ever measured is hovering over the North Pole
A strong polar vortex in early 2020 led to what may be a record-breaking hole in the ozone layer over the Arctic.
-
 Life
LifeThe Great Barrier Reef is suffering its most widespread bleaching ever recorded
Major bleaching events are recurring with increasing frequency on the Great Barrier Reef, hindering its recovery.
-
 Space
SpaceRed giant stars that eat planets might shine less brightly
Some stars may shine less brightly after ingesting a planet. That finding, if confirmed, could have implications for calculating cosmic distances.
-
 Space
SpaceSaturn’s auroras may explain the planet’s weirdly hot upper atmosphere
Data from NASA’s Cassini spacecraft could help solve Saturn’s mysterious “energy crisis.”
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsQuantum mechanics means some black hole orbits are impossible to predict
Computer simulations reveal that foreseeing the paths of three orbiting objects sometimes requires precision better than the quantum limit.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCan plasma from recovered COVID-19 patients treat the sick?
Researchers are racing to set up clinical trials of antibody-rich convalescent plasma from recovered patients to treat or prevent COVID-19.