News
-
 Earth
EarthGreenland and Antarctica are gaining ice inland, but still losing it overall
Inland ice accumulation is not enough to counteract the amount of ice melting off Antarctica and Greenland into the oceans, satellite data show.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe sun is less magnetically active than similar stars, and we don’t know why
Why our star seems so different from its stellar kin is a mystery.
-
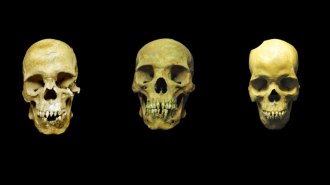 Anthropology
Anthropology16th century skeletons suggest the slave trade brought some diseases to Mexico
Slaves buried in a 16th century grave in Mexico had hepatitis B and yaws, suggesting the slave trade helped spread some versions of those diseases.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRemdesivir is the first drug found to block the coronavirus
Preliminary results suggest that an antiviral treatment speeds recovery from COVID-19.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTo end social distancing, the U.S. must dramatically ramp up contact tracing
Life after social distancing may involve apps that ask you to self-isolate after you’ve been near someone who tests positive for COVID-19.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyA ‘crazy beast’ from the time of dinosaurs belongs to an obscure mammal group
Paleontologists have finally matched a bizarre fossil, Adalatherium hui, to an obscure group of ancient mammals called gondwanatherians.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologySpinosaurus fossil tail suggests dinosaurs were swimmers after all
Unique among known dinosaurs, Spinosaurus had a finlike tail, which the predator may have used to propel itself through the water.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVaping may damage the heart just as smoking does
Vapers and smokers showed similar signs of blood vessel damage, compared with people who didn’t smoke or vape.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHere’s why a hero shrew has the sturdiest spine of any mammal
The hero shrew’s rigid backbone is among the weirdest mammal spines, its incredible strength aided by fortified vertebrae bones.
By Jake Buehler -
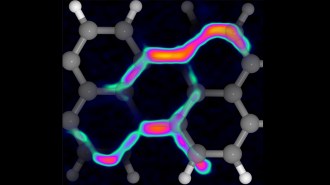 Physics
PhysicsScientists ‘strummed’ a molecule’s chemical bonds like guitar strings
Scientists dragged an atomic force microscope tip, with a single carbon monoxide molecule dangling from it, across a chemical bond.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat coronavirus antibody tests tell us — and what they don’t
Antibody tests can give a clearer picture of who has been infected but don’t guarantee immunity for those who test positive.
-
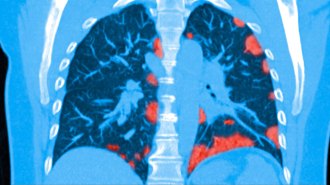 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSome patients who survive COVID-19 may suffer lasting lung damage
Results from a study in China suggest that some COVID-19 patients will be left with long-term lung problems.
By David Cox