News
-
 Life
LifeFish poop exposes what eats the destructive crown-of-thorns starfish
During population booms, crown-of-thorns can devastate coral reefs. Identifying predators of the coral polyp slurpers could help protect the reefs.
By Jake Buehler -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyWhat the 1960s civil rights protests can teach us about fighting racism today
Princeton political scientist Omar Wasow talks about how his research into violent versus nonviolent protests applies to the current moment.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Animals
Animals5 reasons you might be seeing more wildlife during the COVID-19 pandemic
From rats and coyotes in the streets to birds in the trees, people are noticing more animals than ever during the time of the coronavirus.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTaking hydroxychloroquine may not prevent COVID-19 after exposure
Hydroxychloroquine didn’t protect health-care workers from getting sick after being exposed to someone with COVID-19, a new study shows.
-
 Climate
ClimateRapid sea level rise could drown protective mangrove forests by 2100
Mangroves have kept up with rising water so far, but new research reveals their limits.
-
 Space
SpaceA Milky Way flash implicates magnetars as a source of fast radio bursts
A bright radio burst seen from a magnetar in the Milky Way suggests that similar objects produce the mysterious fast radio bursts observed in other galaxies.
-
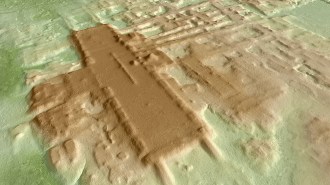 Humans
HumansLidar reveals the oldest and biggest Maya structure yet found
A previously unknown Maya site in Mexico, called Aguada Fénix, adds to evidence that massive public works may have preceded kings in the civilization.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat parents need to know about kids in the summer of COVID-19
So far, evidence suggests children don’t often get severely ill from COVID-19, but there’s more to learn about their role in its spread.
-
 Life
LifeThese tube-shaped creatures may be the earliest known parasites
Fossils from over 500 million years ago might be the first known example of parasitism in the fossil record, though the evidence isn’t conclusive.
-
 Humans
HumansThe Dead Sea Scrolls contain genetic clues to their origins
Animal DNA is providing researchers with hints on how to assemble what amounts to a giant jigsaw puzzle of ancient manuscript fragments.
By Bruce Bower -
 Earth
EarthChicxulub collision put Earth’s crust in hot water for over a million years
An asteroid impact 66 million years ago caused hot fluids to circulate in the crust, creating conditions that may have been ideal for microbial life.
-
 Space
SpaceA weird cosmic flare called the ‘Cow’ now has company
Scientists have now found three similar luminous, short-lived bursts of light, part of a class known as fast blue optical transients.