News
-
 Oceans
OceansThese ancient seafloor microbes woke up after over 100 million years
Scientists discover that microbes that had lain dormant in the seafloor for millions of years can revive and multiply.
-
 Physics
PhysicsA black hole circling a wormhole would emit weird gravitational waves
A new calculation reveals the strange gravitational waves LIGO and Virgo could see if a black hole were falling into a hypothetical tunnel in spacetime.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA wasp was caught on camera attacking and killing a baby bird
Some wasps scavenge carrion or pluck parasites off birds, but reports of attacks on live birds are rare.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA popular heartburn medicine doesn’t work as a COVID-19 antiviral
In lab tests, an antacid didn’t prevent coronavirus infection, but clinical tests are needed to see if it can help people who already have COVID-19.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe star cluster closest to Earth is in its death throes
Gaia spacecraft observations of stars’ motion within and fleeing the cluster suggest the 680-million-year-old Hyades has only 30 million years left.
By Ken Croswell -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAncient DNA suggests Vikings may have been plagued by smallpox
Viral genetic material from human remains provides direct evidence that smallpox infected people dating back to the year 603.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMasks help new moms with COVID-19 safely breastfeed their babies
A study reports newborns could be held and breastfed safely when moms with COVID-19 wore masks and cleaned their hands.
-
 Earth
EarthCOVID-19 lockdowns dramatically reduced seismic noise from humans
Human-caused seismic activity was reduced by as much as 50 percent around the globe during lockdowns as a result of the coronavirus pandemic.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTo prevent the next pandemic, we might need to cut down fewer trees
Investing in halting deforestation and limiting the wildlife trade could be a cost-effective way to reduce the risk of pandemics, a new analysis finds.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyAn ancient skull hints crocodiles swam from Africa to the Americas
A group of crocs, or at least one pregnant female, may have made a transatlantic journey millions of years ago to colonize new land.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyStone artifacts hint that humans reached the Americas surprisingly early
Finds uncovered in a Mexican cave suggest North America may have had human inhabitants more than 30,000 years ago — way before archaeologists thought.
-
 Astronomy
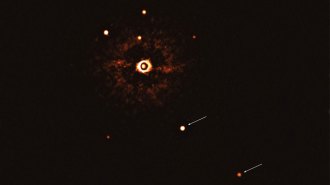
AstronomyThis is the first picture of a sunlike star with multiple exoplanets
A first family portrait reveals a weird cousin of the solar system: a star about the mass of the sun orbited — distantly — by two massive gas giants.