News
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyAstronomers detect the brightest ever fast radio burst
The fast radio burst came from 130 million light-years away. That proximity allowed an in-depth search for what produced the mysterious signal.
-
 Animals
AnimalsTiny thumbnails may be key for rodents’ global takeover
Thumbnails might have boosted rodents’ food-handling skills, helping them thrive worldwide.
-
 Life
LifeA sixth mass extinction? Not so fast, some scientists say
A new analysis suggests that recent extinctions have been rare, limited mostly to islands and slowing. But others argue this is all just semantics.
By Jake Buehler - Animals
Here’s how fruit flies’ giant sperm squeeze into tight spaces
Researchers found that fruit fly sperm push against one another and align in orderly bundles, preventing knots that could block reproduction.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyVenice’s iconic winged lion statue originated in ancient China
European artisans turned a Tang Dynasty tomb guardian sculpture into a symbol of medieval Venetian statehood, researchers say.
By Bruce Bower -
 Microbes
MicrobesAntarctic lake microbes have flexible survival strategies
Life teems under the Antarctic ice sheet. In subglacial Lake Mercer, it is surprisingly versatile and isolated from the rest of the world.
By Douglas Fox -
 Animals
AnimalsThis lizard can tolerate extreme levels of lead
Cuban brown anoles have the highest blood lead levels of any vertebrate known — three times that of the previous record holder, the Nile crocodile.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA cold today helps keep the COVID away
A recent cold appears to be a defense against COVID-19 and a partial explanation for kids’ tendency toward milder coronavirus infections.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA bioengineered protein may someday treat carbon monoxide poisoning
Mice treated with the protein, which is found in bacteria, quickly eliminated carbon monoxide from their body in their pee.
-
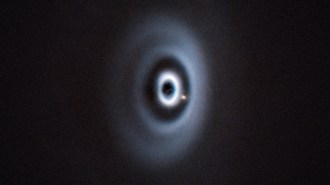 Astronomy
AstronomyA newborn planet munches on gas and dust surrounding its host star
In a first, astronomers imaged a baby planet within a gap in the disk of material around a star, confirming predictions about how rings form.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentRiver turbulence can push toxic pollutants into the air
Levels of hydrogen sulfide gas soared near a raging section of the Tijuana River in San Diego, exposing residents to potentially harmful air pollution.
-
 Life
LifeHorses may have become rideable with the help of a genetic mutation
To make horses rideable during domestication, people may have inadvertently targeted a mutation in horses to strengthen their backs and their balance.
By Jake Buehler