News
-
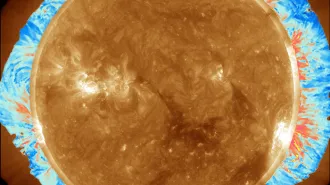 Astronomy
AstronomyCheck out the first-ever map of the solar corona’s magnetic field
Solar physicists watched waves in the sun’s corona to map the whole corona’s magnetic field. Future observers could use the same technique to predict solar eruptions.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyThis ichthyosaur died after devouring a creature nearly as long as itself
Ichthyosaurs, marine reptiles generally thought to munch on soft prey like cephalopods, may have chowed down on fellow big marine reptiles, too.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyX-rays reveal what ancient animal mummies keep under wraps
A new method of 3-D scanning mummified animals reveals life and death details for a snake, a bird and a cat.
-
 Humans
HumansAncient sculptures hint at universal facial expressions across cultures
Interpreting the emotions carved onto sculptures from long ago offers a new way to study how humans perceive facial expressions.
By Bruce Bower -
 Tech
TechMethanol fuel gives this tiny beetle bot the freedom to roam
A new robot insect uses energy-dense methanol as fuel, not batteries. It could be a blueprint for future search-and-rescue bots with long run times.
By Carmen Drahl -
 Animals
AnimalsCulling dingoes with poison may be making them bigger
Meat laced with toxic powder has been used for decades to kill dingoes. Now, dingoes in baited areas are changing: They’re getting bigger.
By Jake Buehler -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDust can spread influenza among guinea pigs, raising coronavirus questions
In three out of 12 guinea pig pairs, an animal coated in influenza virus, but immune to infection, spread the virus to another rodent through dust.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyIn a first, astronomers spotted a space rock turning into a comet
Scientists have caught a space rock in the act of shifting from a Kuiper Belt object to a comet. That process won’t be complete until 2063.
-
 Earth
EarthDeath Valley hits 130° F, the hottest recorded temperature on Earth since 1931
Amid a heat wave in the western United States, California’s Death Valley is back in the record books with the third hottest temperature ever recorded.
-
 Life
LifeHow two new fungus species got named after the COVID-19 pandemic
Tiny fuzz on a beetle and fake leopard spots on palms now have Latin names that will forever nod to the new coronavirus.
By Susan Milius -
 Astronomy
AstronomyHubble watched a lunar eclipse to see Earth from an alien’s perspective
Hubble observed sunlight filtering through Earth’s atmosphere during a lunar eclipse to see what a habitable exoplanet’s atmosphere might look like.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyInterfaith soccer teams eased Muslim-Christian tensions — to a point
Soccer bonded Christian and Muslim teammates in Iraq, but that camaraderie didn’t change attitudes.
By Sujata Gupta