News
-
 Animals
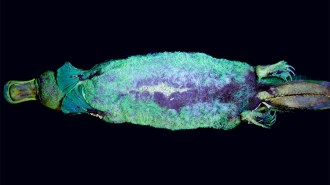
AnimalsA blue-green glow adds to platypuses’ long list of bizarre features
The discovery of platypuses’ fluorescent fur has researchers wondering if the trait is more widespread among mammals than anyone has realized.
-
 Life
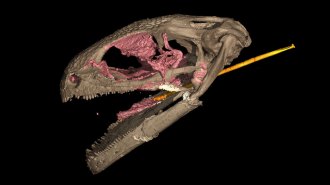
LifeAn ancient amphibian is the oldest known animal with a slingshot tongue
A tiny amphibian that lived 99 million years ago waited for invertebrate prey before snatching them with a swift, shooting tongue.
-
 Space
SpaceThe Milky Way makes little galaxies bloom, then snuffs them out
When dwarf galaxies cross the Milky Way’s frontier, our galaxy compresses their gas, sparking star birth, but then robs them of their star-making gas.
By Ken Croswell -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyFemale big-game hunters may have been surprisingly common in the ancient Americas
A Peruvian burial that indicates that women speared large prey as early as 9,000 years ago sheds new light on gender roles of ancient hunter-gatherers.
By Bruce Bower -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyWhy South America’s ancient mammals may have lost out to northern counterparts
When North and South America joined millions of years ago, mammals from the north fared better in the meetup. Extinctions in the south may be why.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
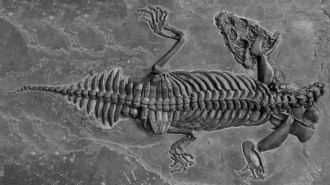
AnimalsA surprisingly tiny ancient sea monster lurked in shallow waters
Scientists have found a new species of marine reptiles called nothosaurs from around 240 million years ago.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA fish’s fins may be as sensitive to touch as fingertips
Newfound parallels between fins and fingers suggest that touch-sensing limbs evolved early, setting the stage for a shared way to sense surroundings.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCOVID-19’s death rate in the U.S. could spike as new cases soar
Effective treatments are one possible reason the mortality rate from COVID-19 fell over the summer. Rising cases could reverse the trend.
-
 Health & Medicine
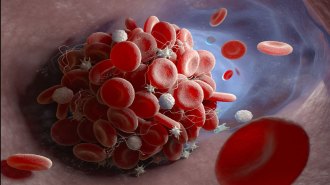
Health & MedicineHow COVID-19 may trigger dangerous blood clots
Clots may stem from net-casting immune cells that, instead of fighting a coronavirus infection, capture red blood cells and platelets.
-
 Space
SpaceJupiter may host atmospheric ‘sprites’ or ‘elves’ never seen beyond Earth
For the first time, NASA’s Juno spacecraft may have spied the bright, superfast light show on another world.
-
 Psychology
Psychology‘Deaths of despair’ are rising. It’s time to define despair
A sense of defeat, not mental ailments, may be derailing the lives of less-educated people in the United States.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsHow frigid lizards falling from trees revealed the reptiles’ growing cold tolerance
Some Florida lizards’ ability to handle temperatures down to 5.5° C may provide clues to how they might deal with the extremes of climate change.