News
-
 Environment
EnvironmentHow planting 70 million eelgrass seeds led to an ecosystem’s rapid recovery
The study is a blueprint for restoration efforts that capitalize on seagrass habitats’ capacity to store carbon and that can be replicated elsewhere.
-
 Physics
PhysicsThe first room-temperature superconductor has finally been found
A compound of carbon, hydrogen and sulfur conducts electricity without resistance up to 15° C, but there’s a catch: It works only under high pressure.
-
 Plants
PlantsHow Venus flytraps store short-term ‘memories’ of prey
Glowing Venus flytraps reveal how calcium buildup in the cells of leaves acts as a short-term “memory” that helps the plants identify prey.
-
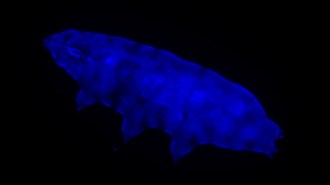 Animals
AnimalsGlowing blue helps shield this tardigrade from harmful ultraviolet light
Tardigrades have a newly discovered trick up their sleeve: fluorescence.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPufferfish may be carving mysterious ‘crop circles’ near Australia
In 2011, scientists discovered that tiny pufferfish were sculpting Japan’s underwater “mystery circles.” Now, more circles have emerged in Australia.
By Jake Buehler -
 Physics
PhysicsFundamental constants place a new speed limit on sound
Physicists propose a new maximum rate that sound waves can travel under conditions normally found on Earth — 36 kilometers per second.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyEasy interventions like revamping forms help people show up to court
A new study shows that simple behavioral interventions called nudges can help people avoid a missed court appearance and resulting arrest warrant.
By Sujata Gupta -
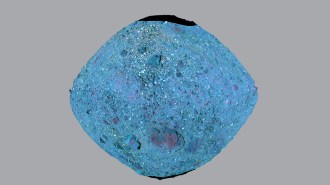 Space
SpaceThe asteroid Bennu’s brittle boulders may make grabbing a sample easier
NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft is about to collect a bit of asteroid Bennu. Here’s why it’s good that new research suggests its boulders are brittle.
-
 Oceans
OceansLarge-scale changes in Earth’s climate may originate in the Pacific
A new study suggests that the melting of Alaska’s glaciers into the North Pacific could have far-ranging effects on ocean circulation and the climate.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyNeandertal babies had stocky chests like their parents
Our evolutionary relatives may have inherited short, deep rib cages from their ancient ancestors.
By Bruce Bower -
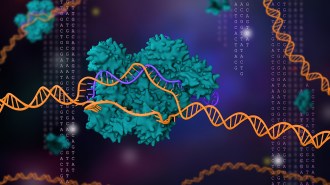 Genetics
GeneticsGene-editing tool CRISPR wins the chemistry Nobel
A gene-editing tool developed just eight years ago that has “revolutionized the life sciences” nabbed the 2020 Nobel Prize in chemistry.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyBones from an Iron Age massacre paint a violent picture of prehistoric Europe
Bones left unburied, and in one case still wearing jewelry, after a massacre add to evidence that prehistoric Europe was a violent place.