News
-
 Space
SpaceWater exists on sunny parts of the moon, scientists confirm
New observations of the moon, made by a telescope flying onboard a Boeing 747-SP jet, have confirmed the presence of water on sunlit areas of the moon.
-
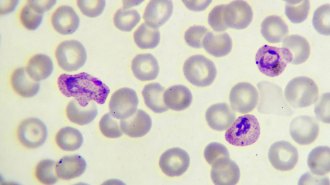 Microbes
MicrobesHow malaria parasites hide from the human immune system
By turning genes on or off, the parasite keeps blood levels low but persistent, so infection doesn’t set off alarm bells for the immune system.
-
 Humans
HumansThe longest trail of fossilized human footprints hints at a risky Ice Age trek
Researchers have discovered the world's longest trail of fossilized human footprints at White Sands National Park, New Mexico.
-
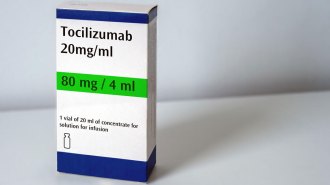 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe arthritis drug tocilizumab doesn’t appear to help fight COVID-19
The best available evidence so far hasn’t found that the anti-inflammatory drug benefited patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyBat-winged dinosaurs were clumsy fliers
The two known species of bat-winged dinosaurs were a dead end when it comes to the evolution of bird flight, a new study finds.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHomo erectus, not humans, may have invented the barbed bone point
Carved artifacts excavated from Tanzania’s Olduvai Gorge suggest now-extinct hominids made barbed bone points long before humans did, researchers say.
By Bruce Bower -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHow environmental changes may have helped make ancient humans more adaptable
An East African sediment core unveils ecological changes underlying a key Stone Age transition.
By Bruce Bower -
 Space
SpaceNASA’s OSIRIS-REx survived its risky mission to grab a piece of an asteroid
NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft just tried to grab a piece of asteroid Bennu. If successful, the spacecraft will return the sample to Earth in 2023.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe diabolical ironclad beetle can survive getting run over by a car. Here’s how
The diabolical ironclad beetle is an incredibly tough little creature. A peek inside its exoskeleton reveals what makes it virtually uncrushable.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNaked mole-rats invade neighboring colonies and steal babies
Naked mole-rats invade neighboring colonies, steal pups and evict any others left behind. The show of force may be central to their underground lifestyle.
By Jake Buehler -
 Oceans
OceansEven the deepest, coldest parts of the ocean are getting warmer
Deep-sea temperatures seem to be rising, but it’s too soon to say whether that’s a result of climate change caused by humans, researchers say.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFire ants build little syphons out of sand to feed without drowning
To escape a watery death, some fire ants use build sand structures that draw the insects’ sugary, liquid food out of containers and to a safer place.